In this article, we discuss Farm Digesters and the Role of Biogas in the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions.
What are the Benefits of Farm Digesters?
Farmers and the local community can benefit greatly from on-farm digesters.
Farmers may use digesters to better control nutrients, reduce odours and methane emissions, and increase farm profitability.
Dairy, swine, and poultry are the most common animal kinds on biogas digester equipped farms.
What Digester Technologies are Used on Farms?
The most common digester system technologies on farms in the United States are:
- complete mix (CSTRs),
- covered lagoons, and
- plug flow.
On farms, the type of digester employed is usually dictated by the waste management procedures in place as well as the type of animal dung fed into the digester. Biogas is frequently collected from anaerobic digester systems and utilised to:
- create electricity,
- feed boilers or furnaces, or
- offer combined heat and power.
In the United States, roughly 300 digesters are in use on cattle ranches (2021).

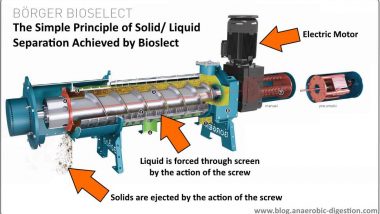
What are the Main Components of Farm Digesters?
Farm Digesters usually comprise:
- one or more digester chambers,
- a slurry preparation facility,
- storage for the processed slurry,
- a gas-collecting space, and
- an area for the mechanical equipment needed for slurry heating and agitation.
Those are the main components of an anaerobic digester system for biogas generation on a farm.
Because this and associated equipment will require inspection, adjustment, and maintenance, ease of access to the various components should be stressed.
Original article first published in July 2017:
Methane Emissions from Agriculture
 Agriculture is the largest source of methane emissions in Britain, adding the equivalent of over 17m tonnes of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere every year.
Agriculture is the largest source of methane emissions in Britain, adding the equivalent of over 17m tonnes of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere every year.
A large proportion of that methane comes from livestock, especially cattle.
Anaerobic Digesters cannot prevent all those methane emissions. Some of the methane comes directly from the digestive systems of the animals themselves, especially ruminants such as cattle, by enteric fermentation.
How Anaerobic Digestion (AD) in Farm Digesters Can Reduce Agricultural Methane Greenhouse Gas Emissions
But, Anaerobic Digestion Plants can reduce those emissions in a number of different ways.
- They trap and use the large amounts of methane that would otherwise be produced naturally when raw slurry or farmyard manure is stored, or spread on the land. This prevents it from escaping into the atmosphere.
- They allow the nutrients in livestock and other organic wastes to be more effectively used and recycled. This reduces the amount of fossil energy that is consumed, and therefore the greenhouse gases are given off, in the manufacture and transport of artificial fertilizer. (These emissions are in addition to the figure given above, of emissions relating directly to agriculture.) Recycling nutrients will also assist, to some extent, to reduce emissions of nitrous oxide.
- They produce compost fibre which can help to reduce the use of peat in horticulture. This saves on the carbon dioxide emissions given off through peat extraction and use.

Thedifference between these overall savings in emissions, and those saved by generating electricity from gas produced by energy crops, instead of fossil fuels, is very significant.
This is a quotation from the book “Farm Digesters”, by Jonathan Letcher.
Citations in support of these statements – again from the above book:
This is clearly illustrated by a bar chart produced by the German Energy Department.
The bar chart compares the net emissions produced by generating 1 kWh of electricity using three different sources of energy.
These are:
- An average of the fossil fuel types usually used for power generation in Germany (coal, natural gas, etc)
- A digester running purely on specially grown energy crops, such as maize silage and 3) a digester running on a mixture of 40 per cent energy crops and 60 per cent livestock slurry.
The bar chart offsets actual emissions against reductions, if any, created by the process in question. Credit is given in the chart for reductions in the use of artificial fertilizer, for instance, or of methane and other emissions which would have been given off by slurry if it had not been processed in a digester. The results are very revealing.
Carbon Emissions from Farm Digester Fossil Fuel Combustion Compared with GHG Reduction Achieved During Farm Digestion
In generating 1 kWh, the averaged fossil fuels give off emissions equivalent to 0.7kg of carbon dioxide, while the energy crops produce net emissions of 0.45kg. The net emissions from the mixture of slurry and energy crops, by comparison, are less than 0.1kg. Unfortunately, the chart does not include a digester running on livestock waste alone.

But a new study by Bangor University estimates that generating 1 kWh of electricity from a digester processing cattle slurry alone reduces overall greenhouse gas emissions by the equivalent of 3.27 kg of Carbon Dioxide.
In other words, for each 1 kWh of output, the digester running purely on energy crops adds 0.45kg of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, whereas a digester processing livestock waste alone reduces net greenhouse gas emissions by 3.27 kg C02e.
These figures show that processing livestock waste in a digester is a more effective way of reducing greenhouse gas emissions than using energy crops alone.
That is the outcome even though energy crops produce more energy from a given size of the digester.
To read the full content, we recommend the purchase of the excellent book “Farm Digesters”, by Jonathan Letcher, from Green Books.







Should really have a flash arrestor or a water bubbler.
�O�k�.� �t�h�i�s� �i�s� �a�l�l� �v�e�r�y� �g�o�o�d� �b�u�t�.� �G�r�e�e�n�w�a�s�h� �o�f�t�e�n� �s�e�r�v�e�s� �a�s� �a� �f�o�r�m� �o�f� �b�r�a�n�d�-�b�u�i�l�d�i�n�g� �t�h�a�t� �h�a�s� �b�e�c�o�m�e� �i�n�c�r�e�a�s�i�n�g�l�y� �p�o�p�u�l�a�r�.� �
Great article, but have you looked at electric vehicles? Electric vehicles are a great investment when it comes to green technology and helping the environment. Even though they can cost thousands of dollars more than regular vehicles of the same type the benefits in the end are much more rewarding. You save a lot of money on gas and you help out the environment a lot as well.
Where is the evidence that this reduces carbon emissions?