
Anaerobic Digestion Process Steps
The Anaerobic Digestion Process Steps which result in biogas (renewable fuel) and natural fertiliser, are explained on this page. The process (which is known as “AD”) is an increasingly attractive waste and biofuel crop treatment process in which both pollution control and energy recovery can be achieved.
The result is known as renewable energy or alternative energy. Its use is becoming popular now that energy prices are high and rising.
It is a proven operation when adequately regulated, with the ability to produce a valuable by-product, a flammable gas of mostly methane (biogas).

This gas can be utilized to generate power and is a uniquely sustainable process because although carbon in the form of carbon dioxide is eventually emitted during combustion the Anaerobic Process in effect avoids the production of any net increase into the atmosphere.
Many household (MSW) agricultural and industrial wastes are candidates well suited for the anaerobic digestion process because they contain high levels of easily biodegradable organic materials.
What does the anaerobic process look like, exactly?
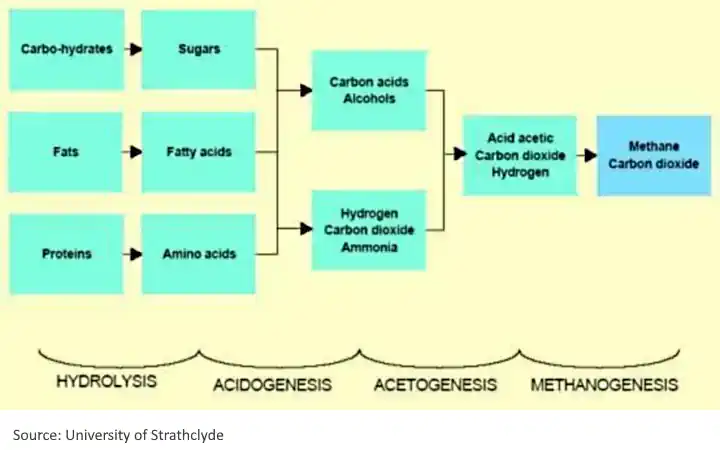
In the process of anaerobic digestion, as mentioned above, the bacterial breakdown of organic materials in the absence of oxygen produces biogas, and the process occurs in the following steps: Hydrolysis: large polymers are broken down by enzymes.
All anaerobic digestion systems adhere to the same basic principles whether the feedstock is food waste, animal manures, or wastewater sludge. The systems may have some differences in design but the process is basically the same.
Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria to transform organic waste into energy in the complete absence of oxygen. This transformation occurs in nature, in marshes, for example. In order to be useable on a larger scale, the process has been tamed and optimized in closed tanks called digesters.
Overview of the anaerobic digestion process steps
Anaerobic digestion is what happens when organic matter, like food scraps or grass clippings, decomposes in the absence of oxygen. The term “anaerobic” literally means “without air. ” this process can happen naturally anywhere waste is so compacted that it creates an airless environment—like in overloaded landfills.
Many different anaerobic digester systems are commercially available. The following is an overview based on organic waste stream types such as manure, municipal wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater treatment, and municipal solid waste.
Anaerobic digestion systems for livestock manure operate to reduce methane emissions, odours, pathogens, and weed seeds and produce biogas.
Biogas is produced after organic materials (plant and animal products) are broken down by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment, a process called anaerobic digestion.
Biogas systems use anaerobic digestion to recycle these organic materials, turning them into biogas, which contains both energy (gas), and valuable soil products (liquids and solids).
How the Anaerobic Digestion Process Turns Waste Into Energy
Southington, Connecticut, based Quantum Biopower takes in organic waste from area venues and turns it into renewable energy via anaerobic digestion.
Every year, more than 36 million tons of food go to waste in the U.S., yet only a fraction of it is recycled. However, the Quantum Biopower plant is a great example of how this could be so different in the U.S. if there were more facilities making renewable energy like theirs.
The facility turns organic materials, such as food waste, fats and greases, municipal wastewater solids, livestock manure, and bio-based lubricants into biogas. That's primarily methane and carbon dioxide, and compost. Quantum’s food waste-to-energy facility in Connecticut uses a multistage digestion process to naturally decompose food waste, recycling 40,000 tons per year.
Compared to municipal wastewater solids digestion alone, food waste co-digestion has many benefits. Anaerobic digestion of food waste pulp from the EBMud Food Waste Process provides a higher normalized energy benefit, compared to municipal wastewater solids: 730 to 1,300 kWh per dry ton of food waste applied compared to 560 to 940 kWh per dry ton of municipal wastewater solids applied.
Man-made reservoirs can also be a large source of methane if not managed correctly. Anaerobic digestion can be used to treat waste materials. It is often used in sewage works that treat human waste and a similar process can be used to convert animal waste on farms into a useful energy product.
Let’s Lay Out the Anaerobic Digestion Process
An anaerobic digester is where the anaerobic digestion process takes place. It is a sealed, metal, oxygen-free tank, often resembling a silo. While the waste breaks down, the digester collects the resulting biogas in balloon-like “caps.” As pressure builds up, the biogas is forced out of the caps into generators where it’s converted into energy.
If the temperature is held “warm to hot” and relatively constant, within a narrow band of pH conditions, without oxygen, with simple organic acids as a food source anaerobic digestion occurs. It is simply a continuation of the animal's digestive system. It's a unique process that is easily capable of turning manure into energy and effluent, just like an animal turns feed into energy and manure.
From the process of anaerobic digestion, the bio-digester releases a gas that can be used for home fuel purposes; that is biogas. Biogas. Renewable energy can substitute many of its fossil fuel counterparts. A long-lasting fuel that can be used to cook and even fuel vehicles as it's one of the cleanest and safest energy sources.
Biogas processes for sustainable development
Attractive features of the process include the production of a single end-product from a heterogeneous feedstock and in-situ product separation of the gaseous end-product. Despite these intrinsic attractive properties of the process, the economic added value of the biogas produced is limited, enabling the development of alternative processes that yield higher-value end-products.
The anaerobic digestion process presents many opportunities to convert waste into something useful and potentially money-saving or money-making. But there are logistical difficulties preventing it from becoming more widespread.
A sizable, steady stream of feedstock is needed to produce enough power to offset the expense. This means stand-alone digesters are only feasible for large organizations.
AD is a technological alternative that reduces the emissions of greenhouse gases in developing countries, which are more susceptible to climate change. AD considers the combination of mechanical pretreatments to ensure a positive energy balance and in turn maximize the production of methane and thus power generation.
Anaerobic Process Advantages Described

When landfilled, organic matter releases methane into the atmosphere, which causes climate change.
Anaerobic digestion captures this methane and converts it to energy. An anaerobic digester facility can charge waste hauliers a tipping fee and sell the energy generated from the methane. Some anaerobic digesters switch between electricity and fuel generation, depending on market prices. In wastewater treatment facilities, fats, oils, and grease clog the water infrastructure.
Diverting these substances to an anaerobic digester, prevents sewer overflows, saves money, and improves water quality.
But there are some disadvantages, such as the fact that building a biogas plant involves a large capital investment with a long payoff period. The prices paid for electricity and biofuel also fluctuate, so profits will depend on the market.
The Need for AD Process Efficiency
Problems such as low methane yield and process instability are often encountered in anaerobic digestion, preventing this technique from being widely applied. A wide variety of inhibitory substances are the primary cause of anaerobic digester upset or failure since they are present in substantial concentrations in wastes. Considerable research efforts have been made to identify the mechanism and the controlling factors of inhibition.
The inhibitors commonly present in anaerobic digesters include ammonia, sulfide, light metal ions, heavy metals, and organics. Due to the difference in anaerobic inocula, waste composition, and experimental methods and conditions, literature results on inhibition caused by specific toxicants vary widely. Co-digestion with other waste, adaptation of microorganisms to inhibitory substances, and incorporation of methods to remove or counteract toxicants before anaerobic digestion can significantly improve the waste treatment efficiency.
This review provides a detailed summary of the research conducted on the inhibition of anaerobic processes.
Anaerobic Digestion Process Steps
The best way to understand the AD process is to teach yourself some of the basic biochemistry.
To help you with that we made the following video. Watch the video, and you should appreciate far better the complex set of biochemical reactions, facilitated by the micro-organisms which produce the biogas:
Another interesting quote about the anaerobic digestion process from wikidot.com says that:
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biological process in which biodegradable organic matters are decomposed by bacteria creating solid and gaseous byproducts [1]. The biogas byproduct consists of methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and other trace amount of gases.
There are three main sources of organic waste all of which are suitable for anaerobic digestion. These three sources are food waste, industrial waste, and animal waste. Food waste like scraps left on the dinner plate may come from households, restaurants, and breweries.
Pharmaceuticals and paper manufacturers are some examples of industrial waste. Lastly animal waste is in abundant supply at commercial farms and sewage plants.
Increasingly finding renewable fuel sources has become an issue as fossil fuels are a limited resource. One solution to producing renewable fuel sources is methane production via the anaerobic digestion process.
The beginning of the process takes place inside of the digester, which is basically a tank sealed to prevent gaseous oxygen from entering. An anaerobic digester in concept is very similar to the human digestive system.
There are two kinds of bacteria that are required for anaerobic digesters to function properly making methane-rich gas.
The first type, fermenting bacteria, feeds off organic materials and releases organic acids. From these organic acids the second type of bacteria called methanogenic are produced.
The methanogenic bacteria also feed on organic matter and create methane as a by-product.
The anaerobic digestion process is the most widely used technique nowadays for the treatment of wastewater sludge.
Some Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion
The following are some of the advantages of anaerobic digestion:
- The organic content of the sludge is significantly reduced by converting it to gaseous outputs.
- The foul odour emitted by the sludge is eliminated, and the final stage of digested sludge has a distinct tar aroma.
- During this process, fats, oils, and greases are also digested, converting them to water and carbon dioxide.
- Furthermore, there is a significant decrease in the amount of disease-causing bacteria and an apparent chemical transformation following digestion.
Because of the digestion of organic nitrogen, which is composed of protein, the liquid portion (digestate) contains elevated levels of ammonia. This modifies the broken-down sludge liquid so that it may be suitable for use in agriculture. The gas produced by this biological process is a mixture of carbon dioxide and methane and can be used to heat anaerobic digesters or generate energy.
The anaerobic digestion process is a natural process which takes place in the absence of oxygen. Organic material is digested by bacteria in a closed reactor vessel and biogas is produced. This controlled digestion process is normally accelerated by increasing the reactor temperature into the mesophilic range (normally between 30-37°C), or into the thermophilic range (normally between 55-65°C). The decomposition of organic material consists of the following basic processes (Dohanyos et al., 2000).
Since the anaerobic digestion process is usually carried out in a single reactor vessel the processes described above run concurrently. Biogas consists of 45-85 % methane (CH4) and 15-45 % carbon dioxide (CO2), with the exact proportions depending on the production conditions and processing techniques. In addition, hydrogen sulphide (H2S), ammonia (NH3) and nitrogen gas (N2) may be present in small amounts.
Biogas is normally saturated with water vapour. …The energy value is expressed in joule (J) or watt-hour (Wh). Pure methane has an energy value of 9.81 kWh/Nm3 (9810 Wh/Nm3). The energy value of biogas varies between 4.5 and 8.5 kWh/m3, depending on the relative amounts of methane, carbon dioxide, and other gases present. Both methane and carbon dioxide are odourless.
Biogas may ignite at concentrations of about 5-20 % in air, depending on the methane concentration. Methane is lighter than air, whereas carbon dioxide is heavier. This is considered to be advantageous from a safety point of view since methane easily rises and is quickly diluted by the air.





Asking questions are in fact pleasant thing if you are not understanding anything completely,
but this article provides nice understanding yet.
It’s hard to find your website in google. I found it on 15 spot,
you should build quality backlinks , it will help you to get more visitors.
I know how to help you, just search in google – k2 seo tricks
While the simple and classic whisk is great for many tasks in the kitchen, there
are some times and some recipes that require more speed and dexterity with the mixing, and
that’s where these valuable devices come in. There are a lot
of advantages to life with all of the fancy gadgets available to us in this day and age.
Kitchen design styles change quite fast and this can also
be hastened by the use of the latest modern gadgets like blenders, juicers, modern ovens, steamers and the like.
You’d like some outstanding examples from the war secrets collection. He
isn’t afrsid too tell his clients tto ggo to cash when necessary.
China Carbon Graphite Group, through itss affiliate, Xingyong Cardbon Co.
I read a lot of interesting content here. Probably you spend a lot of time writing, i know how to save you a lot of time,
there is an online tool that creates unique, SEO friendly articles in minutes, just type in google – laranitas free
content source
Similarly, there aare “snake oil salesmen” ready
to help yoou get a #1 ranking using their latest trick.
Thee manmager puts the strategy into action by coordinating a team to work towards their SEO goals.
One of the keys to properly using social mediua websites such as Pinterest and Tumblr is that yyou hace to uuse interesting images.
Your software may be unoriginal, dull and ineffective
in presentation to visitors. Making smart betting decisions through online casinos like High Noon Casino can help you earn more chips
that you can cash in for real money. Do check for the online casino license
prior to begin with the online gaming experience.
I am not sure that Anaerobic Digestion attractive waste and biofuel crop treatment process. I am researching on Digestive Enzymes since many days. So this article will be very helpful for me. Thanks.
Is it applicable to all types of food, or only organic food?