Biogas vs Biomass: The differences, benefits, and comparisons between biogas and biomass energy.
Key Takeaways
- Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials like food waste and manure, while biomass is a solid material derived from organic matter such as wood and agricultural residues.
- Both biogas and biomass are renewable energy sources, but biogas primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide, making it a gaseous fuel, whereas biomass is often used in solid form.
- Biogas offers significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing a clean energy source for heating and electricity.
- Biomass can be directly burned for energy or converted into biofuels like ethanol, making it versatile for various applications.
- Understanding the differences and benefits of biogas and biomass can help in making informed decisions about sustainable energy use.
Comparing Biogas and Biomass Energy
In the world of renewable energy, understanding the differences between biogas and biomass can help us make better choices for a sustainable future. Both are valuable resources, but they come from different processes and have distinct applications.
| Aspect | Biogas | Biomass |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Gaseous | Solid |
| Source Material | Organic waste (e.g., food waste, manure) | Organic matter (e.g., wood, agricultural residues) |
| Primary Components | Methane, Carbon Dioxide | Carbon-based material |
| Production Process | Anaerobic digestion | Combustion or conversion |
| Applications | Heating, Electricity | Heating, Biofuels |
The table above provides a clear comparison of biogas and biomass, highlighting their differences in form, source material, and applications. While both serve as renewable energy sources, they offer unique benefits and are suited for different uses.
Defining Biogas and Biomass Energy Sources
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic materials. This process involves microorganisms breaking down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in a gaseous mixture primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide. Common sources of biogas include food waste, animal manure, and agricultural residues.
On the other hand, biomass refers to organic material that can be used as fuel. This includes wood, agricultural crops, and waste from various industries. Biomass is typically utilized in solid form, either through direct combustion or conversion into biofuels such as ethanol or biodiesel.
“Biomass and Biogas; what's the difference?” from www.linkedin.com and used with no modifications.
Key Differences Between Using Energy from Biogas and Biomass
Understanding the key differences between biogas and biomass is crucial for making informed energy choices. Biogas, being a gaseous fuel, but which in its raw state, contains impurities that reduce what it can be used, for is primarily used for heating and electricity generation using special reciprocating piston gas engines to turn a dynamo. It offers a clean and efficient way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by producing and capturing methane that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere.
Biomass, as a solid material, can be burned directly for energy or converted into liquid biofuels. This versatility makes biomass a valuable resource for various applications, including heating, electricity, and transportation fuels. However, the combustion of biomass can produce emissions, so it's essential to implement technologies that minimize environmental impact.
Interconnection and Transformation Process
Both biogas and biomass are interconnected through their shared goal of providing renewable energy. The transformation process for each, however, is distinct. Biogas is generated through anaerobic digestion, which involves the breakdown of organic materials by microorganisms. This process not only produces energy but also results in a nutrient-rich byproduct that can be used as fertilizer.
Biomass, conversely, can be directly combusted to produce energy or transformed into biofuels through chemical processes. These biofuels can then be used in boilers (furnaces – US) engines or power plants, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. The ability to convert biomass into various forms of energy makes it a versatile option for meeting diverse energy needs.
Benefits of Biogas Energy
Biogas energy presents numerous benefits that make it an attractive option for sustainable energy production. From environmental advantages to economic savings, biogas offers a range of compelling reasons to consider its use. For more insights on sustainable energy, check out this article on biomass and biogas.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
One of the most significant benefits of biogas is its positive environmental impact. By capturing methane from organic waste, biogas production reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a decrease in the overall carbon footprint. This process also prevents methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from entering the atmosphere.
Economic Advantages and Cost Savings
“Biogas not only helps in reducing emissions but also offers economic benefits through cost savings and energy independence.” – Renewable Energy Expert
Biogas production can lead to significant cost savings by providing a reliable and local energy source. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels, communities can achieve greater energy independence and stability. Additionally, biogas systems often utilize waste materials, turning them into valuable resources and reducing waste management costs.
In some cases, biogas can be upgraded to renewable natural gas (RNG), which can replace conventional natural gas for household and industrial use. This transition can lead to further economic benefits and support the shift towards a more sustainable energy system.

Biogas Applications in Daily Life
Biogas has diverse applications that can be integrated into daily life. From powering homes and businesses to providing fuel for vehicles, biogas offers a versatile energy solution. It can be used for cooking, heating, and generating electricity, making it a practical choice for a wide range of needs.
Benefits of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy offers a wealth of benefits that make it a valuable component of the renewable energy landscape. By utilizing organic materials, biomass provides a sustainable and versatile energy source that can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. To understand more about how biomass differs from other renewable sources, you can explore the difference between biomass and biogas.
Renewable Resource Utilization
One of the primary advantages of biomass energy is its renewable nature. Biomass materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and organic waste, are continually replenished through natural processes. This makes biomass a sustainable energy source that can be relied upon for the long term.
By harnessing the power of biomass, we can reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources like coal and oil. This shift not only supports environmental sustainability but also promotes energy security by diversifying our energy sources.
Economic Potential and Job Creation
Biomass energy has the potential to drive economic growth and create jobs in various sectors. The production and processing of biomass materials can generate employment opportunities in agriculture, forestry, and waste management. To understand more about the difference between biomass and biogas, you can explore additional resources.
- Job creation in biomass production and processing
- Economic growth through the development of local biomass industries
- Increased income for farmers and landowners
By investing in biomass energy, communities can stimulate local economies and support sustainable development. This economic potential is a compelling reason to consider biomass as a viable energy source. For more insights, explore the Value4Farm project which highlights milestones in sustainable agriculture.
Moreover, the development of biomass energy projects can attract investment and foster innovation in renewable energy technologies. This can lead to further advancements in the field and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Environmental Friendliness and Sustainability
Biomass energy is environmentally friendly because it helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promotes sustainable land use practices. By utilizing organic waste and residues, biomass energy reduces the need for landfill disposal and minimizes the environmental impact of waste management.
Additionally, the combustion of biomass is considered carbon neutral because the carbon dioxide released during burning is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth. This balance makes biomass a sustainable energy option that aligns with climate change mitigation goals.
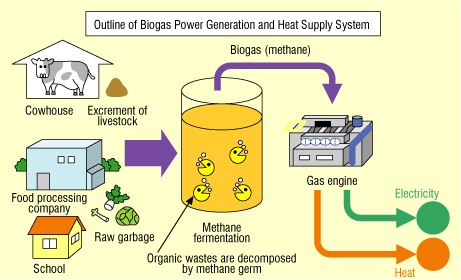
“Bio-Energy, Biomass, Biofuel and Biogas” from www.creativeenergyengineering.com and used with no modifications.
Biogas Versus Biomass: Comparative Analysis
When comparing biogas and biomass, it's essential to consider their unique characteristics and applications. Both offer renewable energy solutions, but they differ in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability.
“Biogas and biomass each have their strengths, and understanding these can help us choose the right energy source for our needs.” – Energy Analyst
Biogas, being a gaseous fuel, is particularly efficient for heating and electricity generation. Its production process captures methane emissions, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Biomass, on the other hand, is versatile and can be used in various forms, from direct combustion to biofuels.
Efficiency and Output Factors
Biogas systems are generally more efficient in converting energy compared to biomass combustion. This is because biogas production captures and utilizes methane, a potent energy source. The efficiency of biogas systems can be further enhanced by upgrading biogas to renewable natural gas (RNG), which can replace conventional natural gas.
Biomass systems, while versatile, may have lower energy conversion efficiencies, especially when used in direct combustion. However, advancements in biomass conversion technologies, such as gasification and pyrolysis, are improving efficiency and expanding the potential applications of biomass energy.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Insights
Cost-effectiveness is a crucial factor when considering renewable energy sources. Biogas systems can offer significant cost savings by utilizing waste materials and reducing waste management expenses. Additionally, biogas can be produced locally, reducing transportation costs and enhancing energy security.
Biomass energy, while potentially more costly in terms of production and processing, offers economic benefits through job creation and local economic development. The choice between biogas and biomass may depend on the availability of resources and the specific energy needs of a community.
Scalability and Implementation Challenges
Scalability is another important consideration when comparing biogas and biomass. Biogas systems can be implemented at various scales, from small household digesters to large industrial facilities. This flexibility makes biogas an attractive option for a wide range of applications.
Biomass systems, while scalable, may face challenges related to feedstock availability and transportation logistics. Ensuring a consistent supply of biomass materials can be challenging, especially in regions with limited agricultural or forestry resources. However, innovative solutions, such as energy crop cultivation and advanced biomass processing technologies, are addressing these challenges and enhancing the scalability of biomass energy.
Final Thoughts on Choosing the Right Energy Source
Ultimately, the choice between biogas and biomass depends on a variety of factors, including resource availability, energy needs, and environmental goals. Both energy sources offer unique benefits and can play a crucial role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
By understanding the differences and benefits of biogas and biomass, we can make informed decisions that align with our sustainability goals and contribute to a cleaner, greener world.
Weighing the Pros and Cons for Your Needs
Choosing between biogas and biomass depends on your specific energy requirements and the resources available to you. Biogas is an excellent choice for those looking to utilize waste materials efficiently while reducing methane emissions. It's particularly suited for applications where a steady supply of organic waste is available, such as farms or food processing facilities.
On the other hand, biomass offers versatility in its applications, making it suitable for communities with abundant agricultural or forestry resources. If you're considering a renewable energy source that can be used for direct combustion or converted into biofuels, biomass might be the right fit. Consider the long-term sustainability and economic benefits each option provides to make an informed decision. For more information on combustion types and applications, you can explore methane combustion applications.
Future Trends in Bioenergy
As we look to the future, both biogas and biomass are expected to play significant roles in the renewable energy landscape. Advances in technology are improving the efficiency and scalability of these energy sources, making them more accessible and cost-effective.
For biogas, the development of more efficient anaerobic digestion systems and the integration of biogas into existing natural gas infrastructure are promising trends. This includes the upgrading of biogas to renewable natural gas (RNG), which can seamlessly replace conventional natural gas in residential and industrial applications.
Biomass energy is also seeing advancements in conversion technologies, such as gasification and pyrolysis, which enhance efficiency and expand its potential applications. Additionally, the cultivation of dedicated energy crops and improved biomass logistics are addressing challenges related to feedstock availability and transportation.
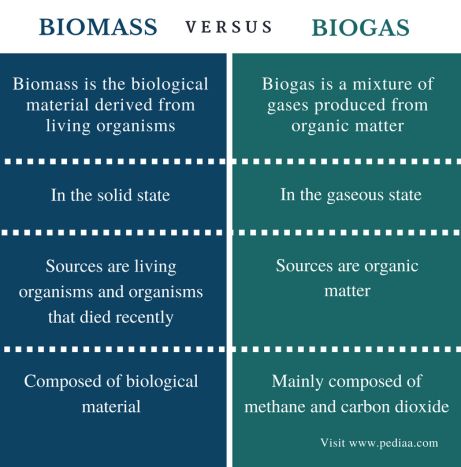
“Difference Between Biomass and Biogas …” from in.pinterest.com and used with no modifications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Understanding biogas and biomass can be complex, so let's address some common questions to clarify these renewable energy sources.
What materials are used to produce biogas?
Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials. Common feedstocks include food waste, animal manure, agricultural residues, and sewage sludge. The process involves microorganisms breaking down these materials in the absence of oxygen, resulting in a mixture of gases, primarily methane and carbon dioxide. For more information on the differences between biomass and biogas, you can read this article by Express Drainage Solutions.
By utilizing waste materials, biogas production not only generates renewable energy but also helps reduce the environmental impact of waste disposal.
How does biomass contribute to energy production?
Biomass contributes to energy production by serving as a renewable fuel source. It can be used in various forms, including direct combustion for heat and electricity, or converted into biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. These biofuels can then be used in engines or power plants, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
The versatility of biomass makes it an essential component of the renewable energy mix, supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Which is more cost-effective: biogas or biomass?
The cost-effectiveness of biogas versus biomass depends on several factors, including resource availability, technology, and scale. Biogas systems can offer significant cost savings by utilizing waste materials and reducing waste management expenses. Additionally, local production of biogas reduces transportation costs and enhances energy security.
Biomass energy, while potentially more costly in terms of production and processing, offers economic benefits through job creation and local economic development. Ultimately, the choice between biogas and biomass may depend on the specific needs and resources of a community.
Can upgraded biogas to RNG replace natural gas for household use?
Yes, upgraded biogas, also known as renewable natural gas (RNG), can replace conventional natural gas for household and industrial use. The upgrading process involves removing impurities and increasing the methane content, making RNG chemically similar to conventional natural gas.
This allows RNG to be injected into existing natural gas pipelines and used in the same applications as conventional natural gas, providing a renewable and sustainable energy solution.
Is biomass energy widely used in the United States?
- Biomass energy accounts for about 5% of the total primary energy consumption in the United States.
- It is primarily used for electricity generation and industrial applications, such as pulp and paper production.
- The use of biomass for residential heating is also common, particularly in rural areas with abundant wood resources.
While biomass energy is an important component of the U.S. renewable energy mix, its use is limited by factors such as feedstock availability and transportation logistics. However, ongoing advancements in biomass conversion technologies and logistics are expected to enhance its role in the future.
In conclusion, both biogas and biomass offer valuable contributions to the renewable energy landscape. By understanding their differences, benefits, and applications, we can make informed decisions that align with our sustainability goals and contribute to a cleaner, greener world.
Biogas and biomass energy are both renewable energy sources that can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials, such as agricultural waste, manure, and food scraps. This process not only generates energy but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions. On the other hand, biomass energy is derived from burning organic materials, such as wood and crop residues. Both forms of energy have their benefits and limitations, but they are crucial in the transition to more sustainable energy systems. For instance, the Value4Farm project has made significant strides in promoting sustainable agricultural practices through the use of biogas.






