In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, digester plants have emerged as a pivotal technology. These facilities not only help manage waste but also generate renewable energy, making them a crucial component in the fight against climate change. Other names for these anaerobic digestion process facilities are “biogas digester”, or “biodigester”, and even “biomethane plant”.
Whether you're an environmental enthusiast or simply curious about renewable energy, understanding digester plants can inspire and empower you to advocate for greener solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Digester plants convert organic waste into biogas, a renewable energy source, and digestate, a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
- Anaerobic digestion is the process used in digester plants, where microorganisms break down waste in the absence of oxygen.
- These plants help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere.
- By using digester plants, communities can reduce landfill waste, produce renewable energy, and improve soil health.
- Examples of operational digester plants include Blue Spruce Farm in Vermont and Fair Oaks Farms in Indiana, showcasing successful integration of this technology.
Understanding Digester Plants and Their Role in Renewable Energy
Before diving into the intricacies of digester plants, it's essential to grasp their fundamental role in renewable energy. These plants are designed to process organic waste materials, such as food scraps, animal manure, and agricultural residues, through a process known as anaerobic digestion. This process not only reduces waste but also produces biogas, a clean energy source that can power homes and businesses.
Most importantly, digester plants offer a dual benefit: they tackle waste management challenges while simultaneously providing a renewable energy solution. This makes them an attractive option for communities and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace sustainable practices.
What Are Digester Plants?

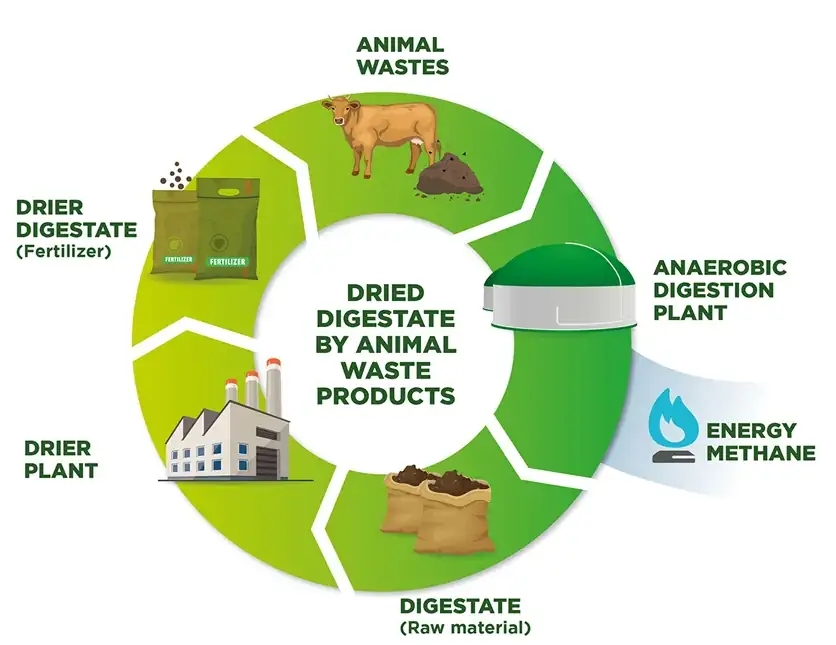
Digester plants, also known as anaerobic digesters, are facilities that utilize microorganisms to break down organic materials in the absence of oxygen. This biological process, called anaerobic digestion, results in the production of biogas—a mixture primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide—and digestate, a nutrient-rich by-product.
The process is simple yet effective. Organic waste is collected and placed in airtight tanks, where bacteria decompose the material. Over time, this decomposition produces biogas, which can be captured and used as a renewable energy source. The remaining solid and liquid digestate can be used as a high-quality fertilizer, enriching soil and promoting sustainable agriculture.

“Anaerobic digestion of solid waste …” from waste-management-world.com and used with no modifications.
How Digesters Work: The Anaerobic Digestion Process
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas and digestate.
In a digester plant, the anaerobic digestion process begins with the collection of organic waste. This waste is fed into a sealed tank, often referred to as a digester, where it undergoes a series of biological reactions. These reactions are facilitated by microorganisms that thrive in oxygen-free environments.
During the digestion process, the microorganisms convert the organic material into biogas and digestate. Biogas, which consists of methane and carbon dioxide, is captured and can be used for various energy applications, such as electricity generation or heating. The digestate, rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, can be applied to agricultural fields to improve soil fertility.
Key Components of a Digester Plant
A digester plant is composed of several key components that work together to facilitate the anaerobic digestion process. These components include:
- Feedstock Collection System: This system gathers organic waste materials, such as food scraps, manure, and crop residues, for processing.
- Digester Tank: An airtight container where the anaerobic digestion process takes place.
- Biogas Collection System: This system captures and stores the biogas produced during digestion for energy use.
- Digestate Handling System: Manages the solid and liquid by-products, preparing them for use as fertilizer.
- Monitoring and Control System: Ensures optimal conditions for digestion by regulating temperature, pH, and other factors.
Uses of Digester Plants in Energy Production
Digester plants play a significant role in renewable energy production by transforming organic waste into valuable resources. The biogas generated through anaerobic digestion can be used in various ways to meet energy needs while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
By converting waste into energy, digester plants help communities achieve energy independence, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and promote a circular economy. This process not only benefits the environment but also offers economic advantages by reducing energy costs and creating new job opportunities in the renewable energy sector. For more on how these systems integrate into the energy landscape, check out the integration of biogas systems.
Biogas Generation and Its Applications
Biogas is a versatile energy source that can be utilized in several applications. It can be burned to generate electricity, used as a heat source, or upgraded to biomethane for use as a vehicle fuel. Additionally, biogas can be injected into the natural gas grid, providing a renewable alternative to conventional natural gas. For more information on the benefits of biogas, you can visit the American Biogas Council.
Because of its versatility, biogas offers numerous benefits for communities and businesses looking to transition to renewable energy sources. It provides a reliable, locally-produced energy option that can help reduce dependence on imported fuels and stabilize energy costs.
Digestate as Fertilizer
Besides producing biogas, digester plants generate digestate, a nutrient-rich by-product that can be used as a natural fertilizer. Digestate contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth. By applying digestate to agricultural fields, farmers can improve soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers.
This practice not only enhances crop yields but also promotes sustainable agriculture by recycling nutrients and reducing chemical inputs. Therefore, digestate plays a crucial role in closing the nutrient loop and supporting environmentally-friendly farming practices. For more insights on how digesters are integrated into sustainable systems, explore the integration of biogas systems into the energy system.

“Digestate Use In The United Kingdom …” from www.biocycle.net and used with no modifications.
Benefits of Digester Plants: Environmental and Economic Impact
Digester plants are transforming the way we handle waste and generate energy. They offer a multitude of environmental and economic benefits that make them a key player in the transition to a sustainable future. By converting waste into valuable resources, these plants help mitigate the negative impacts of waste disposal and fossil fuel consumption.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most significant environmental benefits of digester plants is their ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By capturing methane—a potent greenhouse gas—during the anaerobic digestion process, these facilities prevent it from escaping into the atmosphere. Methane is approximately 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide, making its capture crucial for combating climate change.
Moreover, the biogas produced can replace fossil fuels, further reducing emissions. When used as a substitute for natural gas, biogas significantly lowers the carbon footprint of energy production. Therefore, digester plants play a vital role in reducing the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy use.
Minimizing Odour and Pathogens
Besides reducing emissions, digester plants help minimize odour and pathogens associated with waste. The anaerobic digestion process breaks down organic matter, reducing the odour typically linked with decomposing waste. This is especially beneficial for farms and communities near waste treatment facilities, as it improves air quality and living conditions.
Renewable Fertiliser
- Contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Improves soil fertility and crop yields.
- Reduces reliance on chemical fertilizers, promoting sustainable agriculture.
Digestate, the by-product of anaerobic digestion, serves as an excellent renewable fertilizer. It contains vital nutrients required for plant growth, making it an ideal alternative to synthetic fertilizers. Farmers can apply digestate to fields, enhancing soil fertility and supporting healthy crop production. For more information on how to effectively use digestate, you can read about using biogas slurry as fertilizer.
Using digestate as fertilizer not only benefits agriculture but also closes the nutrient loop, recycling nutrients back into the soil and reducing waste. As a result, it supports sustainable farming practices and contributes to a more circular economy.
Most importantly, digestate helps reduce the environmental impact of agriculture by decreasing the need for chemical fertilizers, which can cause soil degradation and water pollution. By promoting the use of natural fertilizers, digester plants play a crucial role in preserving ecosystems and ensuring food security.
“Sustainable fertiliser from beef …” from www.eitfood.eu and used with no modifications.
Enhancing Soil Health
In addition to providing nutrients, digestate improves soil health by increasing organic matter content. This enhances soil structure, water retention, and microbial activity, leading to healthier and more productive soils. Healthier soils are better able to support diverse plant and animal life, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Energy Independence and Economic Growth
Digester plants contribute to energy independence by producing locally-sourced, renewable energy. Communities can rely on biogas to meet their energy needs, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security. This shift not only benefits the environment but also strengthens local economies by creating jobs and stimulating economic growth.
Furthermore, the construction and operation of digester plants generate employment opportunities in engineering, construction, and plant management. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, so too will the potential for economic development in communities that embrace digester technology.
Examples of Operational Digester Plants
Across the United States, numerous digestion plants are already making a significant impact by turning waste into energy. These facilities serve as inspiring examples of how communities can benefit from embracing renewable energy technologies.
“At Blue Spruce Farm in Vermont, the digester plant processes manure from 1,500 cows, generating enough electricity to power 400 homes. This initiative not only reduces waste but also provides a sustainable energy source for the local community.”
Blue Spruce Farm is a shining example of how digester plants can benefit both agriculture and energy production. By converting manure into biogas, the farm reduces its environmental footprint while contributing to local energy needs.
Blue Spruce Farm, Vermont

“Blue Spruce Farm in Bristol, VT | New …” from www.newenglanddairy.com and used with no modifications.
Blue Spruce Farm in Vermont has been at the forefront of sustainable farming practices for years. Their digester plant processes manure from over 1,500 cows, converting it into biogas that powers homes and businesses in the area. This initiative not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also provides a renewable energy source for the local community.
Freund Farms, Connecticut

“Anaerobic Digester Project Profiles …” from www.epa.gov and used with no modifications.
Freund Farms in Connecticut is another excellent example of a successful digester plant operation. By processing agricultural waste and food scraps, the farm produces biogas used to generate electricity and heat. The farm also utilizes digestate as a natural fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
Fair Oaks Farms, Indiana
![]()
“Anaerobic Digest | BioCycle” from www.biocycle.net and used with no modifications.
Fair Oaks Farms in Indiana showcases the potential of digester plants on a large scale. This innovative farm uses anaerobic digesters to process manure from thousands of dairy cows, generating biogas that powers the farm's operations. The biogas produced is also used to fuel farm vehicles, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to sustainability.
Besides energy production, Fair Oaks Farms makes use of the digestate as fertilizer, improving soil health and crop yields. This closed-loop system not only reduces waste but also enhances the farm's economic viability by lowering energy and fertilizer costs. As a result, Fair Oaks Farms serves as a model for other large-scale agricultural operations seeking to adopt renewable energy practices.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future with Digester Plants
Digester plants represent a vital step toward a sustainable future. By converting waste into renewable energy and valuable by-products, these facilities address environmental challenges while offering economic benefits. Whether on a small family farm or a large commercial operation, digester plants can play a significant role in reducing emissions, enhancing soil health, and promoting energy independence.
As communities and businesses continue to explore renewable energy options, digester plants stand out as a practical and effective solution. By embracing this technology, we can make strides toward a cleaner, greener future, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding digester plants and their benefits can inspire more individuals and communities to adopt this sustainable technology. Here are some common questions about digester plants:
1. How do digester plants contribute to reducing waste?
Digester plants play a crucial role in waste reduction by processing organic materials that would otherwise end up in landfills. Through anaerobic digestion, these plants convert waste into biogas and digestate, effectively reducing the volume of waste and its associated environmental impact.
By diverting organic waste from landfills, digester plants help decrease methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. This not only contributes to cleaner air but also supports efforts to combat climate change.
2. What are the main by-products of anaerobic digestion?
The primary by-products of anaerobic digestion are biogas and digestate. Biogas, a renewable energy source, consists mainly of methane and carbon dioxide. It can be used for electricity generation, heating, or as a vehicle fuel.
Digestate, on the other hand, is a nutrient-rich material that can be used as a natural fertilizer. It contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it an excellent alternative to synthetic fertilizers for agricultural applications.
3. Can digester plants be implemented on small farms?
Yes, digester plants can be implemented on small farms, although the scale and design may differ from larger operations. Small-scale digesters are often designed to handle the specific waste streams of a farm, such as manure from livestock or crop residues.
By adopting digester technology, small farms can reduce waste, generate renewable energy, and produce natural fertilizers, enhancing their sustainability and economic resilience.
4. What types of waste materials are suitable for digestion?
A wide range of organic materials can be processed in digester plants, including animal manure, food scraps, agricultural residues, and wastewater biosolids. The suitability of specific materials depends on the digester design and the desired outcomes.
Co-digestion, which involves combining different types of waste materials, can enhance biogas production and optimize the digestion process. By selecting appropriate feedstocks, digester plants can maximize their efficiency and environmental benefits.
5. How does the use of digester plants affect local communities?
Digester plants can positively impact local communities by providing renewable energy, reducing waste, and creating job opportunities. By converting waste into energy, these facilities contribute to local energy independence and stability.
Moreover, digester plants can improve air quality by reducing odours and emissions associated with waste decomposition. They also support sustainable agriculture by producing natural fertilizers, enhancing soil health, and promoting environmentally-friendly farming practices.
As communities embrace digester technology, they can enjoy the environmental and economic benefits that come with a more sustainable approach to waste management and energy production.




