Anaerobic digestion vs incineration may seem like a strange comparison to make. But now that many people in the waste management industry do, these days, rightfully recognize anaerobic digestion as an alternative, and often much better, alternative to incineration, the comparison of the two waste treatment methods is relevant.
However, navigating the pros and cons of waste treatment methods can be quite a challenge.
Did you know that two prominent methods—anaerobic digestion and incineration—are often compared, and the crucial point considered is their efficiency? This blog will help demystify these processes, comparing them using parameters like energy recovery, environmental impact, and more.
[boomdevs_toc]
Let's dive in to understand which method suits your needs the best!
Key Takeaways
- Anaerobic digestion is a waste treatment method that breaks down waste using bacteria without oxygen, producing biogas for energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Incineration is a waste treatment method that burns waste in an abundance of air to reduce its volume and destroy harmful compounds, but it can cause air pollution, and even when the flue gas is processed to remove the harmful emissions, it requires safe ash disposal.
- When dealing with organic waste, sourced separated organic waste (SSO), and sewage sludge that has a high total solids content, anaerobic digestion works better. On the other hand, incineration may have lower environmental impacts and higher economic performance overall for drier wastes with high plastic contents and high lignin materials, such as non-recyclable wood.
- Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages in terms of energy recovery, environmental impact, and economic factors. The choice between them depends on specific needs and considerations.
- But the truth is that most of the time, burning is not as environmentally friendly as anaerobic digestion (AD) or non-oxidative thermal methods (like pyrolysis, gasification, or hydrothermal processes) since they make CO2 instead of methane. Methane, when used as a non-renewable fuel, is so much more beneficial for its potential to reduce global warming (rather than the damaging effect of CO2) that, for organic wastes, this usually outweighs other considerations.

Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge (Biosolids) versus Incineration of Sewage Sludge
Anaerobic digestion treats sewage sludge, or biosolids, in a special way. It breaks down the waste under high heat with no oxygen. This process produces energy and cuts down on greenhouse gases. But it needs a long residence time and can cause bad smells if the digesters are not managed properly.
On the other hand, incineration burns up the sludge right away. This method shrinks the amount of waste quickly and destroys harmful things in it. But it can pollute the air if not done right and leave behind ash that needs safe disposal.
A study looked at both methods used in China for treating sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). In their study, the researchers discovered that AD of the sludge did the least damage to the environment when it was used before the fiber-rich solid digestate was burned.
However, AD was most sustainable when dealing with sludge with a high total solids (TS) content.
In terms of cost, burning without digestion first was cheaper too, back in the early 2000s. Yet, energy prices are so high now that improvements are being made to cut down on energy use by anaerobic digesters. This improves biogas output from the many profitable AD plants that treat high-TS wastes.
With such changes, experts think we could soon erase the differences between the AD and INC (incineration) methods.

Understanding Waste Treatment Methods
There are two primary waste treatment methods: anaerobic digestion and incineration.
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a way to treat waste. It uses tiny bugs that do not need air. They eat the waste and turn it into biogas. This gas can be used to make power or heat. Waste that has high TS content works best for this process, like sludge from China's sewage plants [Fact 2].
The more of these solids in the waste, the more biogas gets made [Fact 5]. This means less energy is used, which cuts down on costs as well [Facts 3 & 4]. So, anaerobic digestion doesn't just help clean up our mess; it also helps us save money and protects our planet!
Incineration
Incineration is a method used to get rid of waste. First, the waste gets burned. From this burning, heat and sometimes energy get formed. The process also shrinks the size of the waste pile.
The benefits of using incineration are many. One benefit is that it gets rid of harmful stuff in the waste. This makes sure they do not harm people or our planet later on. Also, with less trash to deal with, there's more space left for other things! Another plus is how it can make energy from burning wastes which further cuts down on greenhouse gas emissions.
For facilities looking to handle hazardous waste responsibly, companies like TriHaz Solutions offer compliant, high-integrity incineration services designed to meet strict environmental and safety standards.

Comparing Anaerobic Digestion and Incineration
Anaerobic digestion and incineration are two waste treatment methods that can be compared based on their efficiency, energy recovery, environmental impact, and economic factors.
Anaerobic Digestion vs Incineration: Efficiency and Energy Recovery
Two important things that set the anaerobic digestion followed by incineration of the fibrous residue (ADI) method apart from the incineration (INC) method are efficiency and energy recovery.
| Parameter | Anaerobic Digestion | Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Traditional anaerobic digestion has low carbon conversion efficiency due to the low volatile solids (VS) content of sewage sludge. | For mass reduction efficiency, incineration outperforms anaerobic digestion, but in terms of environmental impacts and economic performance at current high energy prices AD wins. |
| Energy Recovery | Anaerobic digestion using sludge with high total solids (TS) content decreases sacrificial energy consumption significantly. Higher AD efficiency tends to produce more biogas and decrease the operational costs of thermal drying for subsequent incineration of the digestate firbre. | While incineration also recovers energy, the energy gap between ADI and INC (incineration) routes is eliminated at TS contents of 7% or above. |
| Prospects | Sludge with higher VS content (above 60%) exhibits better ecological and economic benefits in anaerobic digestion. | For ADI incineration to reach its peak potential, improved methods need to be adopted to decrease air pollution and manage ash disposal. |
Anaerobic Digestion vs Incineration: Environmental Impact
The environmental impacts of both anaerobic digestion and incineration are significant factors to consider in waste treatment methods.
| Waste Treatment Method | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Anaerobic Digestion | Anaerobic Digestion (ADI) is generally more environmentally friendly, especially when treating sludge with high total solids (TS) content. It has a lower environmental impact compared to the alternative incineration route in China. The method leads to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, with higher Anaerobic Digestion efficiency, there is an associated decrease in energy consumption and operational costs of thermal drying. This is particularly noticeable when treating sludge with a higher volatile solids (VS) content. |
| Incineration Only (INCIN) | Incineration, on the other hand, can lead to air pollution due to the emission of harmful gases and problems with ash disposal. INCIN can contribute to significant environmental degradation if not properly managed. However, incineration has the advantage of destroying harmful compounds that anaerobic digestion might not eliminate. |
Anaerobic Digestion vs Incineration: Economic Factors
When considering the economic aspects of waste treatment, both anaerobic digestion and incineration have costs and benefits.
| Economic Factors | Anaerobic Digestion | Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High initial investment is often necessary, particularly for biogas equipment. For instance, sludge with higher volatile solid (VS) content requires 65% extra capital investment for biogas equipment. | The initial investment for incineration processes can be high, but it may be justified by the significant volume reduction and the potential for the avoidance of microplastic produced during most AD processes. |
| Operational Costs | Anaerobic digestion typically has lower operational costs compared to incineration, and its efficiency can decrease energy consumption and operational costs of thermal drying. | Incineration has higher operational costs associated with fuel usage and maintenance of complex equipment. However, these costs can be offset by the significant volumes of waste that can be processed on a small site. |
| Revenue Generation | Anaerobic digestion can create renewable energy in the form of biogas, which, when upgraded to biomethane (renewable natural gas), can be sold back to the grid. The process also creates nutrient-rich biosolids that can be sold as fertiliser. | Incineration can frequently generate thermal energy which can be converted into electricity and sold to the grid, offsetting some of the costs of operation. MSW incineration is an example of high net energy output from incineration, but sewage sludge biosolids have such a high water content that net energy input is normal for biosolids incinerators. |
| Environmental Costs | Anaerobic digestion has a lower environmental impact than incineration and thus reduces the potential for pollution fines or charges. It also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. | Incineration can lead to high environmental costs due to air pollution and the need for ash disposal as hazardous waste into special hazardous waste landfills, which are environmental time-bombs of hazardous materials waiting to escape and pollute the environment once the engineered containment reaches its design life and fails. |
It's worth noting that the economic balance between anaerobic digestion and incineration can be influenced by a range of factors, including the total solids (TS) content and volatile solids (VS) content of the waste being processed.
Advantages of Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion offers several advantages, including energy production, a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, and nutrient recovery. Find out more about how this waste treatment method can benefit the environment and economy.
Energy Production
Anaerobic digestion produces a lot of green energy. This process uses waste to make biogas. The biogas can be used for heat, light, or power. You can also change it into fuel for cars and buses! It is better than incineration because it makes more energy.
But there's one downside: getting the gear to turn waste into gas costs more money upfront than to burn (incinerate) it.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Anaerobic digestion helps cut down on greenhouse gas emissions. This process breaks down waste and turns it into biogas. Biogas is a clean fuel that does not add harmful greenhouse gases to our air when used. Yes, it does create carbon dioxide when burned, but that is renewable carbon that is emitted, is simply part of the natural carbon cycle, and does not contribute to global warming.
Hence, anaerobic digestion makes more of this eco-friendly fuel and less of the bad gases.
Also, anaerobic digestion works well with high-total-solids content sludges. This means there's less energy use in the process, further reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The more organic solid waste you have per cubic metre, the better this method works for our planet!

Nutrient Recovery
Anaerobic digestion offers the advantage of nutrient recovery from sewage sludge. During the digestion process, valuable nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus can be captured and transformed into biofertilizers.
This means that instead of being wasted or causing environmental harm, these nutrients can be reused to enrich soils and support agricultural productivity. Nutrient recovery not only reduces dependence on synthetic fertilizers but also helps in closing the nutrient loop, promoting a more circular economy approach to waste management.
In contrast, incineration does not provide this opportunity for nutrient recovery.
Advantages of Incineration
Incineration offers volume reduction, energy recovery, and the capability to destroy harmful compounds through high-temperature combustion. The concerns about microplastics in biosolids entering farm soils, and eventually into the water environment and the world's oceans are removed when incineration is used.
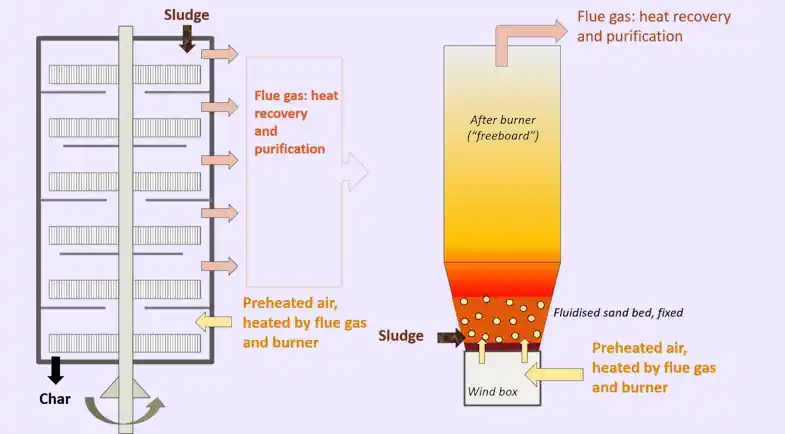
Volume Reduction
Incineration is an effective waste treatment method because it reduces the volume of sewage sludge. This means that a large amount of sludge can be processed and disposed of in a smaller space.
It's important to note that the reduction in volume is particularly beneficial when dealing with high-volatile solid-content sludge, as it can lead to better ecological and economic benefits.
In contrast, anaerobic digestion does not provide significant volume reduction like incineration does.
Energy Recovery
Anaerobic digestion and incineration are waste treatment methods that offer energy recovery. During anaerobic digestion, the organic matter in sewage sludge is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used to generate renewable energy.
The process of anaerobic digestion works better when the sludge has more total solids (TS) and volatile solids (VS). This process reduces energy consumption and operational costs associated with thermal drying.
On the other hand, incineration involves burning sewage sludge at high temperatures to produce heat, which can be converted into electricity or used for other purposes. However, incineration has higher air pollution and ash disposal concerns compared to anaerobic digestion.
In terms of sustainability potential for energy recovery, anaerobic digestion shows greater promise than incineration. The energy gap between these two routes is expected to be eliminated when the sludge's TS content reaches around 7%.
Moreover, the AD route demonstrates more efficient use of energy as it produces more biogas while reducing overall energy consumption and operational costs associated with thermal drying.
Destruction of Harmful Compounds
Incineration is a waste treatment method that involves burning sewage sludge and other waste materials. One advantage of incineration is that it can destroy harmful compounds present in the waste, such as dioxins.
These compounds are known to have negative health effects and can be released into the environment if not properly treated.
Incineration offers a way to safely dispose of these harmful substances, including plastics, through high-temperature combustion, ensuring they do not pose a risk to human health or the environment.
Anaerobic Digestion vs Incineration: Disadvantages of Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion can be disadvantageous due to the long retention time required for effective treatment and the potential for odour issues.
Long Retention Time is Required
Anaerobic digestion requires a long retention time compared to incineration without digestion. This means that the sludge needs to stay in the digester for a longer period of time to fully break down and produce biogas.
In China, the AD route specifically requires a longer retention time for sludge treatment. The length of time needed can vary depending on factors such as the total solids (TS) content and volatile solids (VS) content in the sludge.
Sludge with a higher TS or VS content typically requires a longer retention time for anaerobic digestion. However, despite the longer duration, anaerobic digestion still offers greater sustainability potential, especially when dealing with high-TS content sludge.
Experts completed a life cycle analysis (LCA) study to compare the two ways of breaking down waste. The effects of the longer retention time in anaerobic digestion were looked at.

Potential Odour Issues
One potential disadvantage of anaerobic digestion compared to incineration as a waste treatment method is the possibility of odour issues. Traditional anaerobic digestion processes have low efficiency when it comes to controlling odours.
This means that there is a higher chance of unpleasant smells being emitted during the treatment process. Odour creation can be particularly pronounced in anaerobic digestion systems with a high volatile solid content. But with enclosed AD plant waste reception and digestate processing facilities and good management, any nuisance to neighbours is avoidable.
Disadvantages of Incineration
Incineration of sewage sludge has several disadvantages. It can lead to air pollution, as the combustion process releases pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
Additionally, the disposal of ash generated from incineration can pose challenges, requiring proper management and potential environmental risks.
Air Pollution

Incineration, one waste treatment method, contributes to air pollution. When waste is burned in incinerators, it releases carbon into the atmosphere, which can have negative effects on the environment and human health.
Communities will not be able to meet their net-zero 2050 targets if they rely on incineration, needing to implement expensive and as yet non-proven carbon capture on the incinerator flue gas.
In fact, burning waste in incinerators is a major contributor to a city like London's air pollution crisis. Not only that, but the incineration of municipal solid waste (MSW) and many other wastes without strong environmental regulations to enforce stringent air quality standards emits dangerous substances like dioxin, which pose serious health risks.
Considering these factors, it becomes important to explore alternative waste treatment methods that do not harm our air quality or put our health at risk.
Ash Disposal
Ash disposal is an important consideration when comparing anaerobic digestion and incineration as waste treatment methods. In the case of incineration, ash is generated as a by-product of the process.
This ash contains substances that may be harmful to the environment if not properly managed. It often requires specialized facilities for safe disposal or further treatment. On the other hand, anaerobic digestion does not produce ash as a by-product, reducing the need for additional waste management measures.
This makes anaerobic digestion a potentially more sustainable option in terms of waste disposal.
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples of anaerobic digestion and incineration in practice provides valuable insights into their effectiveness as waste treatment methods. Case studies highlight the benefits and drawbacks of each approach, shedding light on their applications and limitations in different settings.
Anaerobic Digestion in Practice
Anaerobic digestion is a waste treatment method that is already being used in practice. In China, a study compared:
- the anaerobic digestion followed by incineration (ADI) route and
- incineration without digestion (INC) route for sludge treatment.
This confirmed that traditional anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge has low efficiency and a volatile solid content. However, when the total solids content is high, ADI shows greater sustainability potential. It can decrease energy consumption and produce more biogas, which reduces operational costs.
Higher AD efficiency tends to generate more biogas and improve thermal drying performance. This means that anaerobic digestion can be an effective way to treat waste in real-life situations.
Biosolids Incineration in Practice
Incineration of biosolids is a waste treatment method that involves burning sludge to reduce its volume. This process also allows for the recovery of energy from the burn. In practice, incinerators use high temperatures to break down the sludge and destroy harmful compounds.
However, the incineration process can contribute to air pollution due to emissions released during combustion. Additionally, ash disposal is a challenge as it requires proper management and disposal methods.
Despite these drawbacks, incineration has advantages like volume reduction and energy recovery from the burn.
Anaerobic Digestion Vs Incineration: Conclusion
In conclusion, when comparing the waste treatment methods of anaerobic digestion and incineration, there are pros and cons to each. Anaerobic digestion offers advantages such as energy production, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and nutrient recovery.
On the other hand, incineration provides benefits like volume reduction, energy recovery, and the destruction of harmful compounds. The choice between the two methods depends on factors such as efficiency, environmental impact, economic considerations, and specific waste characteristics.
Further research is needed to evaluate the sustainability potential of both methods in different scenarios.
However, in most cases, incineration is less sustainable than anaerobic digestion (AD) or non-oxidative thermal techniques (such as pyrolysis, gasification, or hydrothermal processes) since it produces CO2 rather than methane as the major output.
When used as a nonrenewable fuel, methane is so much more advantageous in terms of its ability to mitigate global warming that it usually overcomes other considerations.
Anaerobic Digestion vs Incineration FAQs
1. What are Anaerobic Digestion and Incineration?
Anaerobic Digestion and incineration are two different ways of treating waste like sewage sludge, bio-waste materials, and the organic fraction of municipal solid waste.
2. How do these methods turn waste into energy?
In anaerobic digestion, bacteria break down wet green bin waste without air to create “green” renewable energy.
In incineration, heat from burning dry mixed municipal solid waste is used to create power.
3. Which method has more environmental benefits?
The life cycle assessment (LCA) shows that both methods lower the amount of carbon released, but anaerobic digestion leads to fewer secondary pollutants and less risk of the eutrophication, which can cause harmful algal blooms.
4. Is there a difference in cost between these two methods?
Yes, with investment and operational costs considered; typically, incinerators have higher initial costs but may have lower operating costs depending on the technology used.
5. Can either method be harmful if not done right?
Yes! Both can be bad for the environment if they are not managed properly. It can be very expensive to clean up the flue gas that incinerators release, and biosolids from anaerobic digestion that have not been treated properly could hurt plants and crops if they are used as fertilizers.
6. Are there any alternatives to these treatment methods?
Other viable options for handling waste include landfilling, pyrolysis, which means heating it up very hot, and hydrothermal carbonization, which uses water under high pressure or produces gas through microbial fuel cells.







