Many waste management professionals face a common question. They need to explain what is the anaerobic process in simple words, without confusing clients or team members. Sometimes, it can be hard to describe how microorganisms work without oxygen or why this matters for energy production and waste treatment.
One interesting fact is that anaerobic respiration produces useful gases like methane and carbon dioxide as by-products. These gases can be captured and used as fuel.
This blog post will explain what is the anaerobic process using easy examples and clear language. It will help you understand its key features, main types, how it works, and where it is used in waste management today.
Read on to learn more about this important topic.
Key Takeaways
- Anaerobic processes happen without oxygen. Microbes break down waste to make gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
- These methods create energy, help treat waste, and reduce landfill volume. In 2022, Europe used anaerobic digestion to treat about 18 million tonnes of biowaste (European Commission).
- By-products include lactic acid in muscles during exercise and ethanol from yeast during fermentation. Methane made from organic waste can become fuel for vehicles or cooking gas.
- The process makes fertiliser called digestate. This helps farms grow healthier crops by recycling nutrients back into the soil.
- Using anaerobic methods saves energy, cuts harmful emissions, and supports sustainable power generation in homes and businesses worldwide.

Key Characteristics of the Anaerobic Process
Anaerobic processes happen without oxygen. They produce energy and create by-products like lactic acid or methane.
Occurs in the absence of oxygen
This process takes place without any oxygen present. Many bacteria use this method to break down organic matter. In waste treatment, these oxygenfree processes can produce gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
Microorganisms act on sludge or food waste in sealed tanks that keep air out.
Anaerobic metabolism helps convert waste into useful products. It also reduces the volume of biodegradable material in landfills. According to the European Commission, anaerobic digestion treated about 18 million tonnes of biowaste across Europe in 2022.
Oxygenfree conditions allow fermentation and biodegradation, turning waste into energy-rich gases.
This method supports both power generation and environmental management for facilities worldwide.
Produces energy
Anaerobic processes produce energy without oxygen. These methods break down organic materials to release energy. In humans, anaerobic respiration occurs during intense exercise. Muscle cells switch to this process for quick energy.
Microorganisms also use anaerobic processes to generate energy through fermentation. They convert sugars into alcohol or acid while releasing gas as a by-product. Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria to turn waste into biogas and fertiliser, providing more efficient waste management options in the industry.
“Flow diagram of the anaerobic digestion …” from www.researchgate.net and used with no modifications.
By-products (lactic acid, ethanol, carbon dioxide, methane)
Anaerobic processes create energy without oxygen. They also produce several by-products.
- Lactic acid is formed during anaerobic respiration in humans. Intense exercise leads to its build-up, causing muscle fatigue.
- Ethanol results from fermentation by yeast and bacteria. This substance is used in alcoholic drinks and as a biofuel.
- Carbon dioxide is released during both anaerobic respiration and fermentation. It can be captured for use in fizzy drinks or as a greenhouse gas.
- Methane is generated during the decomposition of organic matter in anaerobic digestion. This gas can be used as an energy source and for cooking fuel.
Types of Anaerobic Processes
Anaerobic processes come in different forms. They include how humans make energy without oxygen, fermentation by yeast, and the breakdown of waste by microbes.

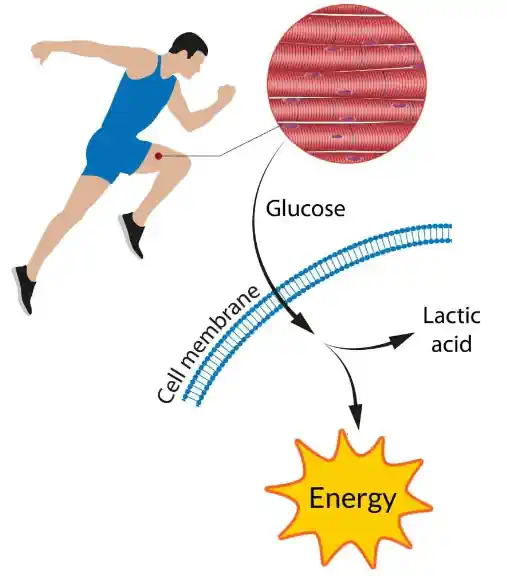
Anaerobic respiration in humans
Humans use anaerobic respiration during high-intensity exercise. This process does not need oxygen to produce energy. Instead, the body breaks down glucose into lactic acid. This happens in muscles when oxygen runs low.
Lactic acid can build up and cause fatigue. Despite this, anaerobic respiration gives quick bursts of energy for short periods. It plays a crucial role in activities like sprinting and weightlifting.
Understanding how this process works helps waste management professionals grasp its impact on human activity and overall health.
“Anaerobic Respiration: Definition …” from www.careerpower.in and used with no modifications.
Fermentation in microorganisms
Fermentation in microorganisms occurs without oxygen. Microbes like yeast or bacteria break down sugars to create energy. This process leads to by-products such as lactic acid, ethanol, carbon dioxide, and methane.
For example, yeast turns glucose into ethanol during beer production.
In waste management, fermentation helps treat organic waste. It reduces the volume of waste while producing useful gases like methane. These gases can be captured and used for power generation or heating.
Understanding fermentation in microorganisms is essential for effective waste treatment processes.
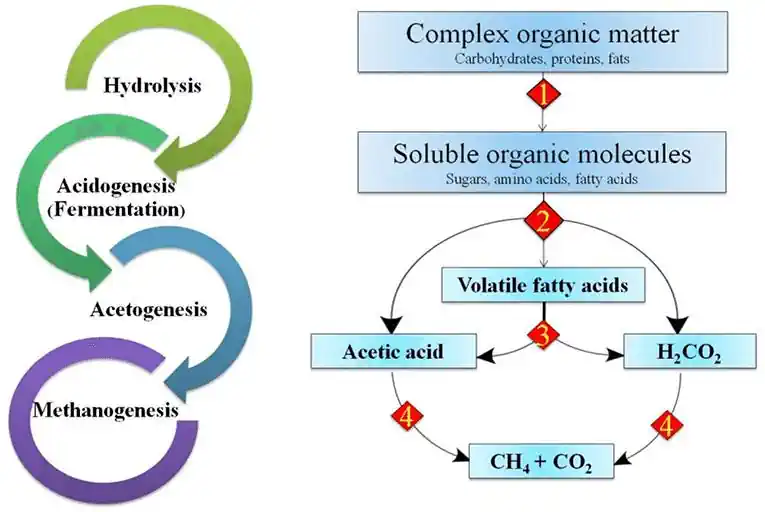
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a key process in waste management. It breaks down organic materials without oxygen. During this process, microorganisms decompose waste and produce biogas. This gas consists mainly of methane and carbon dioxide.
The anaerobic digestion process helps reduce the volume of waste. It also creates energy that can be used for power or heating. The remaining material can become fertiliser, enriching soil health.
Anaerobic digestion plays an important role in managing waste sustainably while generating useful resources.
How Anaerobic Processes Work
Anaerobic processes break down glucose without oxygen. In humans, this creates lactic acid for energy. Yeast also uses glucose to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. These methods are essential for several applications.
Want to learn more about their benefits?

Glucose broken down into lactic acid (Anaerobic respiration)
Glucose is a type of sugar. In anaerobic respiration, glucose breaks down without oxygen. This process happens in muscles during intense exercise. The body needs energy fast but lacks enough oxygen to use aerobic methods.
The breakdown leads to lactic acid formation. Lactic acid can cause muscle fatigue. In some microorganisms, different by-products form, like ethanol and carbon dioxide. These processes are essential in various applications, especially in waste management and bioenergy production.
Yeast breaks down glucose
Anaerobic respiration can be seen in yeast. Yeast cells take in glucose and break it down. They do this without using oxygen. The process creates energy for the yeast to grow and multiply.
As yeast breaks down glucose, it produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. This process is called fermentation. It benefits various industries, including waste management.
Understanding how yeast works helps professionals use it effectively for waste treatment and other applications.

Applications of Anaerobic Processes
Anaerobic processes offer many uses in daily life. They help treat waste and produce energy. These methods create fuel for vehicles and can even provide cooking gas. They also make fertiliser to enrich soil.
Explore how these applications can benefit your work!
Waste and wastewater treatment
Anaerobic processes play a key role in waste and wastewater treatment. They help break down organic matter without oxygen. Microorganisms digest the waste, creating energy while producing useful by-products like methane.
This gas can be used for heating or to generate electricity.
Using anaerobic digestion reduces the volume of waste. It also lowers harmful emissions into the environment. Waste management professionals use this process to improve efficiency and sustainability in their operations.
Understanding these applications leads us to explore power generation next.
Power generation
Waste and wastewater treatment also leads to power generation. Anaerobic processes create energy by breaking down organic waste without oxygen. This process produces biogas, which mainly contains methane.
Biogas can be used to generate electricity and heat.
Using anaerobic digestion in waste management helps turn waste into usable energy. It reduces landfill use while providing a clean fuel source for homes and businesses. Many facilities are now adopting this method for sustainable power generation.
These practices support both the environment and energy needs effectively.
Fuel for vehicles
The process of anaerobic digestion creates methane. This methane can power vehicles. It is a clean fuel option that helps reduce greenhouse gases. Using it cuts down on the need for fossil fuels, which harm the environment.
Many places now use biogas from waste to fuel cars and trucks. This not only makes transport greener but also supports local economies by turning waste into useful energy. As cities grow, finding ways to create sustainable fuel is vital for our future.
The anaerobic process plays a key role in making this happen.
Fertiliser and soil conditioner
Anaerobic processes can create valuable fertiliser and soil conditioners. These products improve soil quality and promote plant growth. When organic waste undergoes anaerobic digestion, it breaks down.
This process produces nutrient-rich digestate. Farmers can use this digestate as a natural fertiliser.

Using anaerobic processes reduces waste. It turns food scraps and other organic matter into useful resources. This benefits the environment by recycling nutrients back into the earth while minimising landfill use.
Fertiliser from these methods supports sustainable farming practices and helps grow healthier crops.

Cooking gas
Fertiliser improves soil health. It helps plants grow better. Cooking gas is another valuable product from anaerobic processes. This gas primarily consists of methane.
Methane forms during the breakdown of organic matter without oxygen. Anaerobic digestion produces large amounts of cooking gas from waste materials like food scraps and animal manure.
Using this gas can reduce reliance on fossil fuels. It can also power stoves and heaters in homes, promoting a cleaner environment for cooking activities.
Conclusion
Anaerobic processes play a vital role in our lives. They happen without oxygen and create useful energy. These processes help treat waste, generate power, and produce cooking gas. Understanding them can lead to better solutions for waste management and energy needs.
Embracing these methods benefits both the environment and society.
FAQs
1. What is the anaerobic process explained simply?
The anaerobic process explained simply, means breaking down matter without using oxygen. This happens in places where there is no air.
2. Where does the anaerobic process take place?
The anaerobic process often takes place in wet soils, animal stomachs, and rubbish heaps where air cannot reach.
3. Why is the anaerobic process important?
The anaerobic process helps recycle waste by turning it into useful things like gas for energy or rich soil for plants.
4. How does the anaerobic process differ from other methods?
Unlike processes that need oxygen, the anaerobic process works in closed spaces with no air and uses special tiny life forms to break down material.





