The quest is on for, not only a clean energy, but one that is also low-cost and truly portable. Adsorbed natural biogas cylinders (ANG) might be the solution.
Many people think capturing and using natural biogas in a green way is hard. But, it's now about to get simpler than you might guess with new adsorbed natural biogas cylinders.
This method can change waste into power that lights up homes and fuels vehicles without harming the planet. This article will show you how one company is unlocking this potential for a brighter, cleaner future.
This knowledge forms the base of our exploration into sustainable energy solutions using adsorbed natural gas technology—providing both insights and action points for those ready to make a change.
Ready? Let’s explore this revolutionary energy option.
Key Takeaways
- Biogas is now being used instead of expensive and dirty fossil fuels thanks to unique patented systems made by Cenergy Solutions. The ANG technology stores methane molecules at high densities and lower pressures than high-pressure CNG tanks.
- It does this by using adsorbents. This lets natural or biogas be put into ANG tanks at low pressures, which cuts down on the cost of high-pressure compression and the risk of putting natural gas (biogas/biomethane) into traditional CNG tanks at high pressures.
- Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) storage uses materials like porous carbon and metal-organic frameworks. This method stores natural gas at lower pressures, making it safer and more efficient than traditional Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
- ANG technology offers a green solution by supporting the use of renewable biogas from organic waste. It helps in reducing harmful emissions and promotes cleaner energy for vehicles and homes.
- Vehicles can go further without needing to refuel thanks to ANG's ability to store more energy in the same space as other methods. Plus, it opens up new possibilities for biomethane storage, contributing to sustainable energy solutions.
- The future of ANG looks promising with ongoing research aimed at overcoming challenges like biogas cleaning. Innovations could lead to higher efficiency and wider adoption across different industries.
- Cenergy Solutions is making strides by using ANG cylinders in Thailand's three-wheel vehicles, showcasing the adaptability of this technology in real-world applications for cleaner transportation options.
Understanding Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG)
Adsorbed Natural Gas, or ANG, offers a smart way to store natural gas at lower pressures compared to Compressed Natural Gas (CNG). It calls for porous materials that grab and hold the gas molecules.
Cenergy Solutions' unique patented solutions are currently replacing fossil fuels with economical and environmentally friendly biogas.
This enables ANG tanks to be filled with natural or biogas at low pressures, lowering the cost of high-pressure compression and eliminating the risk of storing natural or biogas at high pressures in CNG tanks.
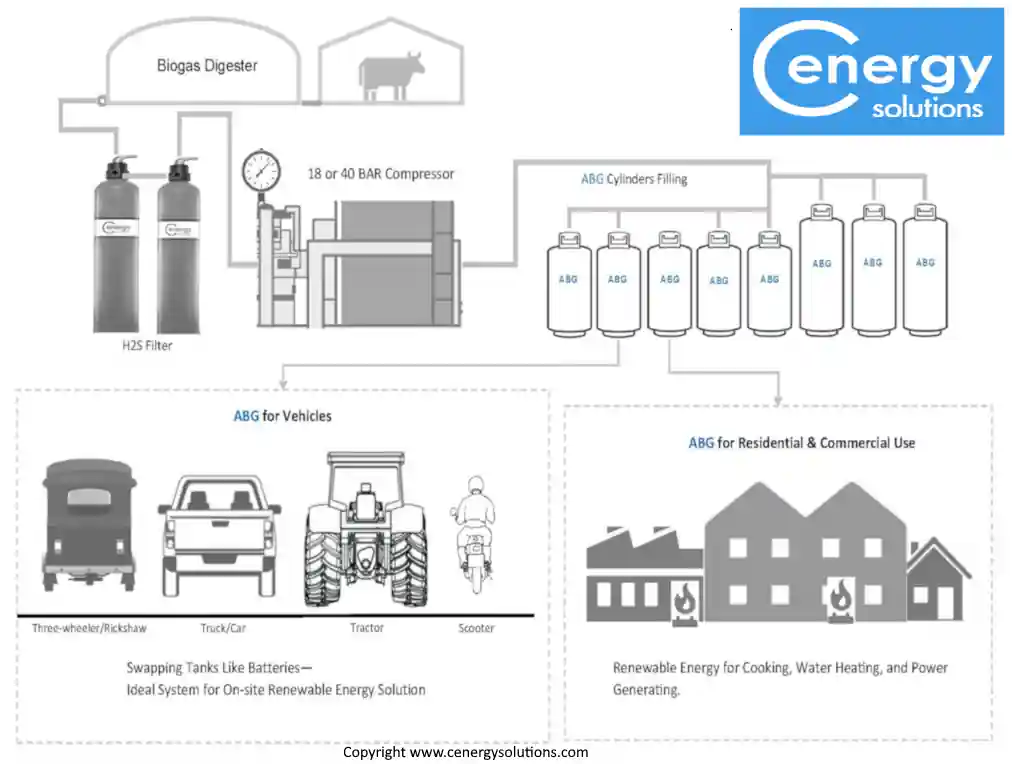
Definition and uses
- Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG)
- A storage technique for natural gas using porous materials. Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) technology uses adsorbents to hold methane molecules at higher densities and lower pressures than high-pressure CNG tanks.
- Materials Used
- Porous carbon
- Metal-organic frameworks
- Covalent organic frameworks
These storage solutions are both safe and lightweight, making them ideal for various applications. The use of ANG can change how we power cars, heat homes, and produce energy from waste.
ANG finds its place in vehicles as an alternative fuel source. It's perfect for light-duty vehicles such as pickup trucks, showing promise for cleaner public transportation options too.
This technology supports the use of renewable biogas—energy made from organic material—thereby offering a greener solution over traditional fossil fuels. With ANG cylinders powering more vehicles on our roads, we can hope to see major strides towards sustainability in our energy consumption habits.
Advantages over other storage techniques
ANG storage stands out because it needs less pressure than compressed natural gas. This makes it cheaper and safer. You don't need costly, high-pressure tanks or complex safety measures.
It's great for vehicles because they can carry more fuel without heavy tanks slowing them down.
Another plus is ANG's ability to hold more energy in the same space. This means cars can drive longer distances without needing a refill. It uses materials like metal-organic frameworks, which are better at catching and holding gas than traditional methods.
Now, let's explore the materials used in ANG storage systems.

Materials Used for ANG Storage
Porous carbon materials and metal-organic frameworks are commonly used for storing ANG. They offer high surface area and strong adsorption capabilities.
Porous carbon materials
Porous carbon-based substances are gaining attention for storing natural gas and biogas. These materials, like activated charcoal, have lots of tiny holes. These holes can hold gases very well.
Activated charcoal is especially good at grabbing carbon dioxide from biogas. This is because it has a lot of space for the gas to stick to and doesn't cost too much.
Scientists are working hard to make these porous adsorption materials even better. They want them to grab more carbon dioxide and still not be expensive. Some of these new materials come from wood waste.
People are also thinking about using them in things like sensors that find out how much of a certain chemical is in a place. This shows that porous carbon-based substances could change how we store gas, offering a cheaper and eco-friendly option compared to squeezing the gas into smaller spaces or cooling it down until it turns liquid.
To watch the following video move forward in the video to 40:19 for an explanation of the benefits ANG technology has meant for Ingevity:
Metal organic frameworks
Metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, are special materials used for storing natural gas. They consist of metal ions linked with organic molecules to form a porous structure. This structure can store gases like methane very well because of its high surface area.
Scientists use MOFs in adsorbed natural biogas cylinders, offering a more efficient way to keep and transport energy.
These frameworks outdo traditional materials such as activated charcoal in gas storage applications. Due to their adjustable nature, researchers can tailor them for specific needs, making them crucial for sustainable energy solutions.
Their unique properties also mean they hold more gas at lower pressures than other methods, simplifying storage and transportation processes while reducing costs.
Covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks, or COFs, are a breakthrough in material science. They consist of interconnected molecular building blocks through strong bonds. This structure makes them unique and highly useful.
Their design is flexible, allowing scientists to tailor them for specific uses. One key feature is their microporous nature, which means they have tiny holes that can trap gases or liquids.
These materials stand out because of their stability and ability to perform under various conditions. Researchers find them fascinating for gas storage applications. They serve well in storing natural gas due to their high surface area and porosity.
These characteristics make COFs ideal candidates for enhancing energy storage technologies and helping with carbon capture efforts—making strides towards more sustainable energy solutions worldwide.
Applications of ANG Technology
ANG technology finds diverse applications in vehicular storage and transportation, serving as an alternative to compressed natural gas (CNG) and presenting a viable option for three-wheel vehicles in Thailand.
Furthermore, its utilisation extends to biomethane storage, enhancing sustainable energy solutions.
Vehicular storage and transportation
Cars need energy to run. This energy can come from different places like petrol or natural biogas. Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) is a smart way to store and move this gas using less pressure than usual methods.
It means trucks and cars can carry more gas with them in a safer, lighter way.
Ingevity and Ozinga Energy are working together to show how ANG can be used in pickup lorries. This project lets these lorries use two types of fuel, increasing their range without needing extra stops for fuelling up.
It's a big step towards making vehicles that are better for our planet.
ANG is a New Alternative to compressed natural gas (CNG)
ANG technology stands as a promising substitute for compressed natural gas. It offers a safe and efficient way to store and transport fuel. This method uses adsorbents like porous carbon materials, which can hold vast amounts of gas at lower pressures than CNG requires.
The result? Vehicles get a bi-fuel system that is both versatile and practical.
Using ANG means cars can carry more fuel without the need for heavy tanks, making it perfect for light-duty vehicles such as pickup trucks and SUVs. This innovation could change how we think about fuel storage in transportation, providing an eco-friendly option that reduces reliance on high-pressure systems.

Use in three-wheel vehicles in Thailand
Cenergy Solutions has harnessed the potential of adsorbed natural/biogas (ANG) cylinders, propelling them as a game-changing solution for three-wheel vehicles in Thailand. This innovative technology presents a low-pressure, bi-fuel alternative designed primarily for light-duty vehicles such as pickup trucks.
With Cenergy at the helm, ANG cylinders are offering an effective and sustainable energy solution tailored towards not only ensuring environmental preservation but also catering to the specific needs of this unique vehicular segment within Thailand.
The use of ANG technology in three-wheel vehicles in Thailand stands as a testament to its adaptability and versatility across diverse vehicular applications, promising substantial contributions towards sustainable energy solutions while navigating complexities within waste management and transportation infrastructure.
Use in biomethane storage
Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) technology holds significant promise for biomethane storage, especially in the context of sustainable energy solutions. As a renewable energy resource predominantly consisting of methane, biogas aligns perfectly with ANG's capacity for effective and environmentally friendly storage.
The application of ANG technology in biomethane storage underscores the potential to provide lower carbon and renewable hydrogen for transport and power generation. This not only offers an alternative to traditional fossil fuels but also contributes towards mitigating carbon emissions, paving the way for cleaner and greener energy solutions.
The use of ANG technology in biomethane storage is emblematic of the industry's endeavour to harness sustainable alternatives by capitalising on advancements in gas adsorption. By enabling efficient storage and release mechanisms for biogas-derived methane, ANG stands as a promising facilitator for transitioning towards more eco-friendly fuel sources, which has profound implications for waste management professionals, environmental researchers, as well as government officials striving to implement sustainable practices within their respective realms.
The Future of ANG Technology
The future of ANG technology holds significant promise for sustainable energy solutions. Advancements in this field can revolutionise natural gas storage, with potential applications ranging from vehicular transportation to biomethane storage.
Ongoing research and development are addressing the challenges to further enhance the effectiveness of ANG technology. Solutions like these adsorbed natural biogas cylinders will be essential if the world is going to meet climate change reduction targets.
Potential for sustainable energy solutions
Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) technology presents an immense potential for sustainable energy solutions. Biogas, when upgraded to produce BioCNG, is a promising alternative fuel that can significantly contribute to sustainable energy solutions.
Innovative technologies utilising green hydrogen and ammonia show great promise in revolutionising the renewable energy landscape. But, unfortunately, they are technologies that require further development before they can be truly useful.
Additionally, the growing interest in solar and wind power further underscores the potential of these sources in driving sustainable energy solutions. But, unlike ANG none of these is available today.
Upgraded community biogas systems offer a practical means of producing and distributing biogas, presenting new opportunities for achieving substantial sustainability gains. The new ANG methodology finally unlocks the full potential of biogas as a renewable energy source, making significant strides towards creating long-term sustainable energy solutions.
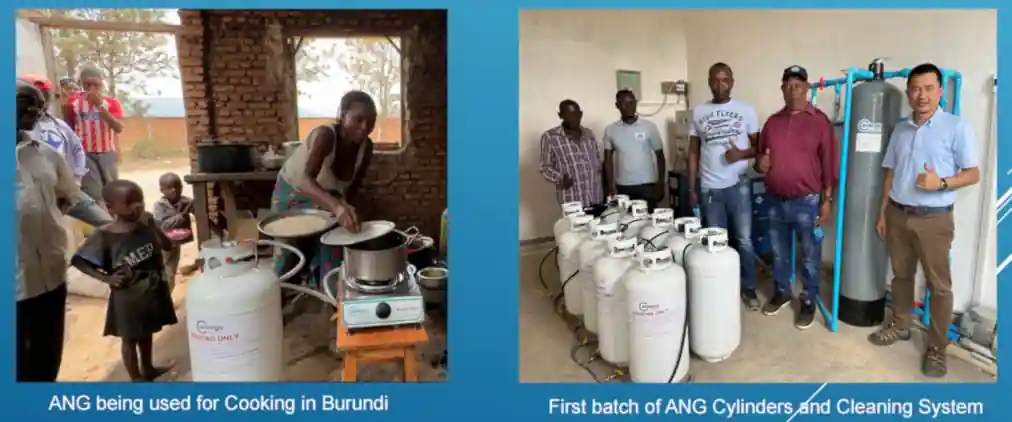

Comparison to traditional gas storage methods
The landscape of gas storage is evolving, shifting toward more efficient and sustainable practices.
This evolution brings into focus the comparison between Adsorbed Natural Gas (ANG) storage methods and traditional approaches. The following table offers a concise comparison.
| Criteria | ANG Storage | Traditional Gas Storage (e.g., Compressed Natural Gas – CNG) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher, due to lower pressure requirements. | Lower, requires high pressure for storage, and stores less densely. |
| Safety | Offers enhanced safety; operates at lower pressures. | Less safe due to high operational pressures. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint encourages the use of biogas. | Somewhat higher carbon emissions from the energy needed to compress at higher pressures & thicker walled cylinders/increased cylinder weight. |
| Storage Materials | Uses advanced materials like porous carbon, and metal-organic frameworks. | Relies on compression alone to achieve liquefaction in heavy steel cylinders. |
| Cost-effectiveness | More competitive, considering long-term operational savings. | May be initially cheaper due to higher availability currently, but costlier in the long run due to energy input for compression. |
| Application Flexibility | Adaptable to various scales, including vehicular and industrial storage. Suitable for light 3-wheeled vehicles, and all larger vehicles. | Primarily focused on large commercial vehicles, vehicle fleets, and industrial applications. |
| Potential for further development of the technology | High, with ongoing research into materials and efficiency. | Low, with established methods leaving little room for innovation. |
This table provides a clear view. It shows that ANG storage boasts several advantages over traditional methods, particularly in efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability. The future of gas storage positively leans towards these innovative solutions. Research and development continue to pave the way for even more promising prospects in the energy sector.
Conclusion
Unlocking the potential of adsorbed natural biogas cylinders holds great promise for sustainable energy solutions. Biomass-based adsorbents could capture CO2 from biogas, contributing to a circular and sustainable economy.
Biogas has significant potential as a renewable energy source for industrial applications, providing an efficient solution to sustainable energy needs. Upgraded community biogas production and distribution systems can achieve a consumption-to-production ratio to unlock the full potential of biogas systems.
Expertise, innovation, and a deep understanding of processes are required to unleash the potential of biogas and biomethane for sustainable energy solutions.
FAQs
1. What are adsorbed natural biogas cylinders?
Adsorbed natural biogas, or ANG, uses a special material to ‘soak up' natural gas like a sponge. This means we can store more gas in less space, making it easier and safer for cars and other vehicles to use this cleaner type of fuel.
2. How does ANG work better than other types of natural gas storage?
ANG stores gas at lower pressures because it uses materials like activated carbons that have lots of tiny holes. These holes hold the gas without needing it to be squished in tightly, unlike CNG (compressed natural gas) which requires high-pressure tanks.
3. Why is ANG considered a sustainable energy solution?
ANG comes from renewable sources and produces fewer pollutants than diesel or petrol when burned in engines. Plus, using materials like covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for storage doesn't harm the environment, helping us take big steps towards cleaner air and less pollution.
4. Can all vehicles use ANG instead of petrol or diesel?
Not right now, but many car makers are looking into how they can make their engines run on this greener fuel. The conversion is not complex or difficult to do. Most cars already designed for compressed natural gas could switch to ANG with a few adjustments.
5. Are there any benefits to drivers who choose ANG-powered vehicles?
Yes! Besides being kinder to our planet by reducing emissions, driving an NGV (natural gas vehicle) might save you money on fuel costs in the long run—especially as governments look into taxing polluting fuels more heavily and subsidising cleaner alternatives like ANG.
6. How do scientists create these amazing materials that store so much gas?
They use really smart chemistry techniques to build structures at the molecular level—think tiny building blocks that fit together perfectly—to maximise space where gases can be stored efficiently through adsorption sites within porous materials such as MOFs (metal-organic frameworks), aerogels, and zeolites.







We want to Buy some cylinders, how much aré they?
To buy the product you must contact Cenergy Solutions here: http://www.cenergysolutions.com/
What is the price of one cylinder and how much kg of gas it has and what is the storage pressure
Hi, Emanuel Acko. The way to get prices is to contact Cenergy direct.