We promise an examination of biomethane its advantages and disadvantages—our honest view of its benefits and drawbacks.
Looking for a way to tackle climate change? A rising number of people consider that biomethane might be part of the answer. This clean, renewable gas reduces greenhouse emissions and our dependence on dirty energy like coal and oil.
Our blog will guide you through the benefits and drawbacks of using biomethane, covering everything from environmental impact to technological challenges. Ready to learn more? Keep reading! We also bring you up-to-date information about the rapid growth of biomethane production in the UK over the period of 2023 to 2024.
Biomethane Advantages and Disadvantages – Key Takeaways
- Biomethane is a renewable energy that comes from organic waste, like food scraps and animal manure. It helps fight climate change by cutting down greenhouse gases.
- Using biomethane can reduce pollution in the soil and water. This makes our planet cleaner and keeps us healthier by preventing diseases.
- There are some challenges with biomethane. It needs new technology to work better, especially in cold weather. Also, it might not be the best choice for crowded cities because of safety concerns.
- Compared to fossil fuels, biomethane is better for the environment. It produces less carbon emissions and uses waste materials to make energy.
- Creating energy from biomethane also supports a circular economy. This means we reuse things instead of throwing them away, leading to less waste and more green jobs.
- Rapid Growth: The UK's biomethane capacity grew by 16.7% in the past year, aligning with international growth rates and expectations set by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Strategic Goals: The UK aims to establish 1,000 new biomethane plants by 2030, with projections suggesting that biomethane will surpass nuclear energy in terms of production by 2031.
- Current Infrastructure: There are currently 720 operational anaerobic digestion (AD) plants in the UK, which process approximately 46 million tonnes of organic material annually, producing around 24 TWh of biogas.
- Efficiency Improvements: The increase in biomethane capacity has been supported by the development of larger, more efficient plants, despite a slight reduction in the total number of plants.
- Energy Security and Sustainability: Biomethane is recognized as a secure, domestically produced energy source that provides a viable alternative to fossil fuels, particularly for heating and transport.
- Future Impact: By 2030, the fully deployed biomethane sector could create 60,000 jobs, save 27 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually, and heat between 4.5 to 6.4 million homes in the UK.
- Support from policymakers: Policymakers are increasingly viewing biomethane as a “no-regrets” renewable energy option that is crucial for reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels and enhancing the dependability of the UK's energy supply.

Advantages of Biomethane
Biomethane is a clean and renewable energy source, reducing soil and water pollution, when compared with spreading farm slurries, like manure on farmland. It is clean-burning and thus does not cause health problems when used to power vehicles. While the process used to create it also produces organic fertilisers, encouraging a circular economy.
1. Clean and renewable energy source
Using waste organic matter, we turn it into biomethane through a process called anaerobic digestion. This method is brilliant because it makes energy without needing new resources from the Earth.
It's a method of recycling garbage into something very useful: clean energy. I've seen how this works at local biogas plants.
It's impressive how food waste, crop residue, animal manure, etc., having been used to produce biogas, once purified by “upgrading” to almost completely just methane, can be injected into standard gas mains, and even make electricity, heating and lighting up homes.
This type of energy doesn't add more harmful gases to the atmosphere, making it a friend to our planet. Since biomethane is chemically the same as natural gas, people can use it to replace “natural gas” in their kitchens for cooking or to keep their houses warm, without harming the environment.
Generating electricity this way also means less reliance on fossil fuels like coal or oil, which can hurt the environment when we use them for power.
Collectively, these actions contribute significantly to combating global climate change and ensuring the well-being of ecosystems worldwide.

2. Production of organic fertilisers
Biogas and its purification to become biomethane turns organic waste into valuable plant food. This process creates an organic digestate, a substance rich in nutrients. Farmers can use this instead of chemical plant foods to grow crops.
It not only boosts plant growth, it has also been shown to help the plants fight off diseases.
Using this method closes the loop in waste management. It shows how we can turn leftovers into useful products again. Organic fertilisers keep soil healthy and reduce our need for harmful chemicals.
Next, let's explore how biomethane encourages a circular economy.
3. Encourages circular economy
Using biomethane helps us reuse items and materials we usually throw away. Kitchen scraps, garden waste, and even animal droppings can be turned into energy instead of ending up in landfills. This process supports a circular economy where we keep resources in use for as long as possible.
By converting organic wastes into renewable natural gas, we make the most of our resources and cut down on greenhouse gases.
This approach not only reduces methane emissions but also promotes sustainable resource management. It shows how smart waste handling can lead to a cleaner planet and more green jobs.
Thinking about waste as a valuable resource leads us to invent better ways to manage it. Now let's delve deeper into some challenges with biomethane production.
Disadvantages of Biomethane
Biomethane technology has limited advancements and can contain impurities, affecting its usability. Additionally, temperature variations can have an impact on biomethane production, which makes it difficult to produce energy consistently.
1. Limited technological advancements
Many systems that turn waste into biogas are not very efficient yet. They struggle in cold weather because they require steady heat. Finding ways to improve these systems is essential for better energy generation from biomethane without depending too much on sacrificial heating using part of their own energy, or heat from external heat sources during colder months.
2. Production affected by temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in biomethane production. Cold climates can significantly reduce the efficiency of biogas generation, requiring additional heat energy to maintain consistent output.
This impact on production necessitates thorough management, considering the temperature variability experienced in different regions. Therefore, understanding and addressing these temperature effects is essential for optimising biomethane production systems.
As waste management professionals and environmental researchers strive for sustainable solutions, mitigating the impact of local ambient temperature fluctuations is imperative to ensuring efficient biogas generation across diverse geographical areas.
3. Not always suitable for dense urban areas
Biomethane isn't ideal for crowded cities due to potential odour issues near biogas plants. The “bad neighbour” odour can be avoided, but to do so requires some additional initial investment and for the operators, from day to day, to take care to contain any odour within the AD plant.
Methane's explosiveness during production and transport requires high precautionary attention to health and safety at work levels, including DSEAR compliance (Engald), making it less suitable for densely populated urban streets.
Comparing Biomethane with Other Energy Sources
When comparing biomethane with other energy sources, it shows lower carbon emissions compared with natural gas and offers potential cost savings and environmental benefits over fossil fuels.
To explore more, continue reading the full article.
1. Lower carbon emissions compared to natural gas
Biomethane emits carbon dioxide when combusted, but the carbon emitted is biogenic carbon, part of the earth's normal carbon cycle, rather than fossil fuel natural gas, reducing greenhouse gases. This makes it an eco-friendly choice for energy production. With this advantage, biomethane can play a key role in combating global warming and supporting sustainable power generation.
Compared to natural gas, biomethane significantly reduces carbon dioxide emissions. This contributes positively to the environment by lowering greenhouse gas levels and promoting cleaner energy sources.
Biomethane's lower carbon footprint highlights its potential as an alternative and renewable energy option while curbing harmful emissions from traditional fossil fuels.
2. Potential cost savings
Biomethane offers substantial cost savings by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, leading to lower associated expenses. Its low production costs result from utilising freely available waste organic matter for energy production, providing further financial benefits.
Additionally, biomethane's role in ensuring energy independence offers potential cost savings by eliminating vulnerability to disruptions in the international energy supply market and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, its implementation and maintenance do not require the development of new technology or infrastructure, potentially resulting in substantial cost savings.
3. Environmental benefits over fossil fuels
Compared to fossil fuels, biomethane offers lower carbon emissions and decreases reliance on non-renewable resources. This renewable energy source contributes to reducing greenhouse gases, and addressing climate change concerns.
By diverting biodegradable waste to biogas plants, it mitigates the environmental impact of landfills, promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to energy generation. This shift towards biomethane aligns with the global push for cleaner and greener energy solutions.
Entities: renewable energy source, biodegradable waste, climate change concerns.
The Rise of Biomethane in the UK: A Sustainable Energy Frontier
In recent years, the United Kingdom has made significant strides in the development of biomethane, also referred to as “green gas.”
This progress is vital as the country navigates the challenges of energy security and environmental sustainability.
In 2022, the UK's biomethane capacity witnessed a remarkable growth of 16.7%, a rate that aligns with the forecasts of the International Energy Agency (IEA) and positions the UK alongside the rapid advancements in Europe and the US.
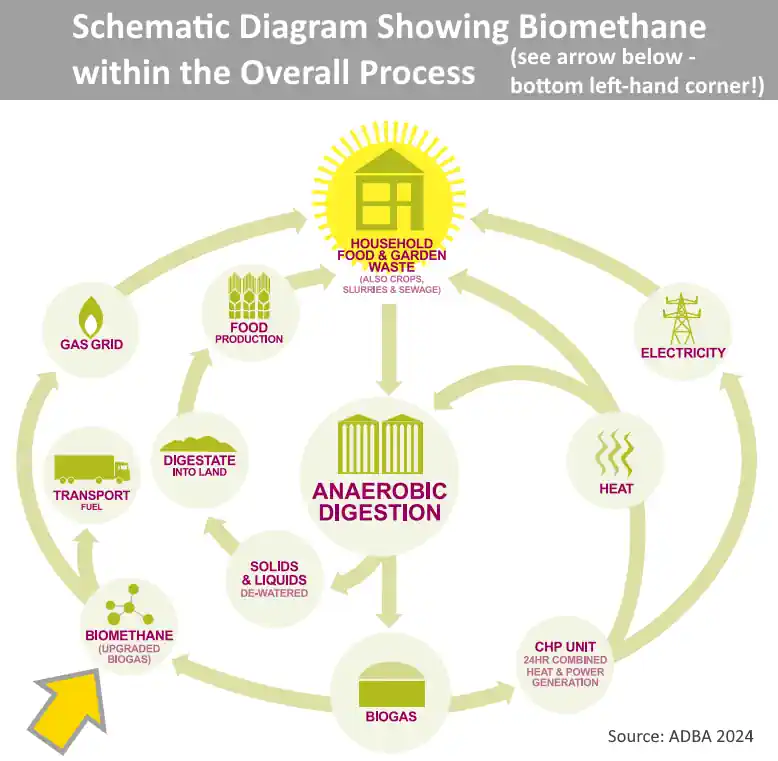
Growth and Projections
The Anaerobic Digestion and Bioresources Association (ADBA), a leading trade body, notes that this growth is not just about numbers—it's about meeting and possibly exceeding international expectations.
The IEA has projected an annual compound growth rate of 22% for the biogas sector, making it the second fastest-growing renewable sector after solar energy.
Chris Huhne, ADBA Chair, emphasizes the sector's robust expansion and its realistic goal to establish 1,000 new biomethane plants by 2030. If this trajectory holds, biomethane is set to surpass the nuclear sector in terms of energy production by 2031.
Current State of the Biomethane Industry
The UK currently boasts 720 operational anaerobic digestion (AD) plants, with a significant presence in Scotland. These facilities collectively process about 46 million tonnes of organic material annually, transforming it into valuable green energy and preventing the emission of potent greenhouse gases.
From this, approximately 24 terawatt-hours (TWh) of biogas are produced each year. The refined product, biomethane, is then either used directly for electricity and heat generation or injected into the national gas grid.
The commissioning of larger-scale facilities, which more than made up for the retirement of smaller, less effective ones, was what drove last year's capacity increase despite a slight decline in the number of plants. This shift towards more substantial and productive plants underscores the industry's focus on enhancing efficiency and output.

The Role of Biomethane in the UK Energy Mix
As it stands, the biomethane sector contributes about 1% to the UK's greenhouse gas savings annually. However, the potential for future impact is substantial. By 2030, the full deployment of the AD and biogas industry could:
- Create 60,000 jobs (30,000 direct and 30,000 indirect).
- Save 27 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually, which is akin to removing a third of all cars from UK roads.
- Heat between 4.5 to 6.4 million homes with the expected 8 billion cubic meters of produced biomethane.
Biomethane Significance and Future Outlook
Policymakers increasingly recognize biomethane as a “no-regrets” renewable energy source. It offers a secure, domestically produced alternative to fossil gas imports, especially crucial for heating and transport fuels. Moreover, biomethane provides reliable energy during peak demand periods, such as cold, dark winter nights, complementing intermittent sources like solar and wind.
In conclusion, the UK's commitment to expanding its biomethane supply is a critical component of its broader strategy to meet energy demands sustainably and securely. With continued support and investment, biomethane can significantly contribute to the nation's renewable energy portfolio, helping the UK transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Source: ADBA PR
Biomethane Advantages and Disadvantages – Conclusion
In conclusion, biomethane offers significant advantages as a renewable and clean energy source. It reduces greenhouse emissions, improves water quality, and enhances waste management.
The simplicity of the technology for production using organic materials makes it practical and efficient for rural and suburban areas. Emphasising its potential impact on reducing respiratory diseases by reducing the use of diesel fuel, and creating green jobs, highlights the importance of embracing biomethane.
For further exploration, readers can dive into additional resources to gain a deeper understanding of this sustainable energy alternative. Making strides towards incorporating biomethane into our energy sector will yield substantial benefits for both the environment and the economy.
Biomethane Advantages and Disadvantages – FAQs
1. What is biomethane and how is it made?
Biomethane comes from the anaerobic decomposition of organic materials like kitchen waste and animal waste in biodigesters, turning them into a renewable source of energy for things like electricity generation.
2. How does biomethane help the environment?
Using biomethane reduces greenhouse gases by cutting down on fossil fuel burning and household air pollution. It's a cleaner alternative to solid fuels, wood burning, and chemical fertilisers.
3. Can we rely on biomethane all the time for our energy needs?
Yes, of all the biomethane advantages and disadvantages is the winning advantage that it can be switched on and off, just like natural gas. It is always available for use, once it has been produced.
4. Are there any risks associated with using biomethane?
Yes, if not managed properly, the storage and use of biomethane can lead to leaks that may corrode equipment or contribute to air pollution; however, these are manageable with proper safety measures.
5. How does producing biomethane compare with other forms of renewable energies?
Biomethane production uses wastes disposal effectively unlike solar energy or wind power which require specific conditions for efficiency but doesn't have zero emissions like those sources do.
6. Does generating electricity from biogas power impact human health?
If not handled correctly, decomposed material used in biogas production could lead to waterborne diseases or food poisoning due to contamination, but it generally contributes less to air pollution compared to traditional gas stoves or boilers.