Gobar gas is also known as “Bio gas” or simply “biogas”. Its main component is animal dung (gobar – India) along with some other organic matter like dead remains of plants and animals. It can be used for cooking, electricity generation and heating purposes.
The Meaning of Gobar Gas
Gobar gas is a type of renewable energy that is produced from organic waste, specifically cow dung.
It is a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels that can be used to generate electricity, heat, and cooking gas. In this article, we will explore the concept of gobar gas plants for homes, their benefits, and how they work.
Biogas and Gobar Gas: What is the Difference Between Them?
Biogas is a general term for gas produced through the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter, while gobar gas specifically refers to biogas derived from cow dung. Both are renewable energy sources, primarily used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation, and can be upgraded to compressed biogas for use in vehicles.
It's a Low-Cost Renewable Fuel Source for Rural Households
It is proving to be a very cost-effective and environment-friendly alternative fuel for rural households.
Despite the lack of public awareness of biogas in general, it can at least go part-way to provide the answer to the energy needs of rural areas. Furthermore, this gas can be produced from regionally available raw materials and recycled waste and is environmentally friendly and pretty much CO2 neutral.
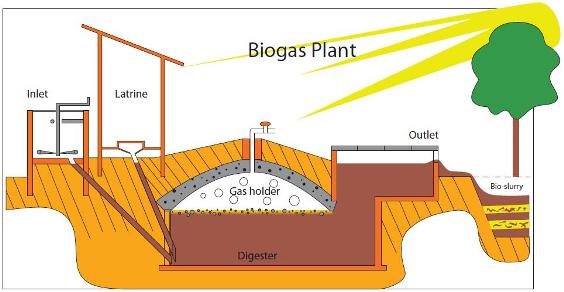
How Does a Gobar Gas Plant Work?
A gobar gas plant works by converting organic waste into biogas through a process called anaerobic digestion. The process involves the following steps:
- Collection of Organic Waste: The first step in the process is the collection of organic waste, such as cow dung, kitchen waste, and agricultural waste.
- Mixing of Organic Waste: The collected waste is mixed with water in a pit or tank to form a slurry.
- Anaerobic Digestion: The slurry is then transferred to a digester tank, where it is sealed and left to ferment for several weeks. During this time, bacteria break down the organic waste, producing biogas and a nutrient-rich slurry called digestate.
- Gas Storage: The biogas produced during the fermentation process is stored in a gas holder, which can be used to supply gas for cooking, lighting, and heating.
- Use of Digestate: The digestate produced during the fermentation process is a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can be used to enrich the soil in agriculture.
Gobar Gas Production in More Detail

In a gobar gas plant, “gobar gas” is obtained by bacterial fermentation of animal refuse. To be a little more specific about the process which makes it. It is produced by the anaerobic digestion or fermentation of biodegradable materials such as manure, sewage, municipal waste, green waste, plant material, and crops. Gobar Gas is a renewable fuel (methane) so it qualifies for renewable energy subsidies in some parts of the world.
When gobar gas is cleaned up by a process called biogas upgrading. After upgrading, the purified biogas is ready to be used as fuel in a massive number of applications from motor car fuel, to running massive gas turbines. Any CNG-converted internal combustion engine can be connected to an alternator to produce electricity. Hence, an easy off-grid electrical power supply which doesn't hasten climate change becomes available to all nations rich and poor.
The heat generated during the combustion of bio gas, or “gobar gas” can be used for use in other processes that require significant heat.

Electricity generated by fuel cells using gobar gas can provide power at night.
This point about gobar gas can be again used in the discussion about the replacement of other sources of electricity like hydropower, thermal power, and nuclear power with biogas energy plants.
This gas supply source can equally be applied to counter-insurgency and stabilization programs with Afghanistan as an example.
The Advantages of Gobar Gas Digesters for India and Similar Nations
Population pressure has practically eliminated India's forests, causing desperate fuel shortages in most rural areas. As a result, up to three-quarters of the country's annual billion tons of manure (India has two cows for every person) are burned for cooking or heating.
This creates enormous medical problems—the drying dung is a dangerous breeding place for flies and the acrid smoke is responsible for widespread eye disease—and deprives the country's soil of vital organic nutrients contained in the manure.
The Gobar (Hindi for “cow dung”) Gas Research Station—established in 1960 as the latest of a long series of Indian experimental projects dating back to the 1930s—has concentrated its efforts, as the name suggests, on generating methane gas from cow manure.
At the station, Ram Bux Singh and his coworkers have designed and put into operation bio-gas plants ranging in output from 100 to 9,000 cubic feet of methane a day. They've installed heating coils, mechanical agitators and filters in some of the generators and experimented with different mixes of manure and vegetable wastes. The results of the project have been meticulously documented and recorded.
This comprehensive eleven-year-long research program has yielded designs for five standardized, basic gobar plants that operate efficiently under widely varying conditions with only minor modifications (see construction details of 100 cubic foot digester that accompany this article).
Ram Bun Singh has compiled much of this information into two booklets, BIO-GAS PLANT and SOME EXPERIMENTS WITH BIO-GAS. via motherearthnews.com
Benefits of a Gobar Gas Plant for Homes and Farms
There are several benefits of installing a gobar gas plant in your home, including:
- Renewable Energy Source: Gobar gas is a renewable source of energy that is produced from organic waste, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly option.
- Cost-effective: Gobar gas plants are relatively inexpensive to install and maintain, and the fuel produced is free, making it a cost-effective alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- Clean Energy: Gobar gas is a clean source of energy that does not produce any harmful emissions, making it a healthier and safer option for households.
- Reduces Waste: Gobar gas plants help to reduce the amount of organic waste that is sent to landfills, reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal.
Summary – The Benefits of Gas from Dung
With the continuing development of science and technology, it is considered that gobar gas will be one of the biggest fuel-providing resources, in the future.
Indeed, introducing a community to a safer, greener, more eco-friendly energy option will make their lives happier, plus much more sustainable in the long run and protect the forests.
This “dung gas” is going through a revolution. It has already, for example, been a quiet engine of ground-level economic transformation in Nepal and numerous other poor Asian and African nations. There are millions of these plants in homes and communities in China as well.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a gobar gas plant for home and farms is a clean, sustainable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
It can help households reduce their environmental impact by providing a renewable source of energy and reducing the amount of organic waste that is sent to landfills.
With the benefits of a gobar gas plant in mind, it is worth considering installing one in your home to enjoy clean, sustainable energy.
Of course, gobar gas has undoubtedly now already, come to stay.
Are you making the best use of it in your farm or rural community?
[Published on 5 September 2019. Updated 5 March 2023, and May 2025.]









You’ve made some really good points there.
I looked on the web for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
If I was to start this project, how much money does it take in investment?
Thanks for this and other excellent post.
I have a presentation to give in January week, and I’m at the look for such information.
Use the dung from sacred cow.
Sir. There has been this scheme 2018 started. THE GOBAR-DHAN SCHEME:
The GOBAR-Dhan Yojana aims to collect cattle waste and solid waste from farmers for sale to entrepreneurs, who there after, will produce manure, biogas and bio-CNG from the waste.
“The scheme will connect farmers to buyers so that farmers can get the right price for dung and agricultural waste,” PM Modi said.